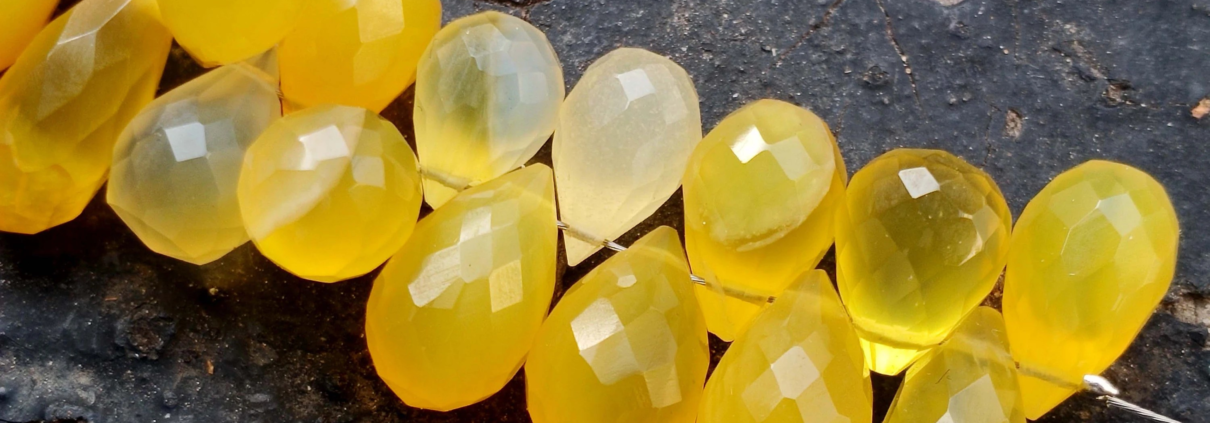
Yellow Chalcedony
Yellow chalcedony is a variety of chalcedony, which itself is a form of microcrystalline quartz. Chalcedony encompasses a broad range of cryptocrystalline quartz varieties that exhibit a waxy luster and translucent appearance. What distinguishes yellow chalcedony is its vibrant yellow color, ranging from pale buttery hues to deeper, more intense tones. This gemstone owes its coloration to the presence of iron impurities.

Overview of Chalcedony Gemstones: Chalcedony gemstones, in general, are a diverse group that includes several varieties, each with its own unique characteristics. The term “chalcedony” is often used as an umbrella to cover stones like agate, carnelian, onyx, and more. These gemstones are popular for their durability, versatility, and the ability to take on various colors.
Agate, for instance, is a type of chalcedony known for its multicolored bands and distinctive patterns. Carnelian, another variety, typically exhibits warm shades of red and orange. Onyx, on the other hand, is recognized for its sleek black appearance. The wide array of chalcedony gemstones makes them prized choices for jewelry and decorative pieces.
Historical Significance: Chalcedony gemstones, including yellow chalcedony, have a rich historical significance that spans cultures and civilizations. In ancient times, these stones were often used for carving intricate cameos and seals due to their relative hardness. They held cultural and religious significance, with beliefs that they could bring about healing, protection, and good fortune.
In ancient Egypt, chalcedony was associated with the goddess Isis and was believed to offer protection against evil forces. Similarly, in ancient Rome, chalcedony was thought to bring courage and emotional balance. The gemstone’s historical use in amulets and talismans reflects the belief in its mystical and protective properties.
In conclusion, yellow chalcedony and its broader family of chalcedony gemstones have captured the imagination of humanity throughout history. Their diverse colors, durability, and cultural significance make them not only stunning adornments but also carriers of tradition and symbolism.
Contents
- Geology and Formation
- Physical Properties
- Applications and Uses
- Mining Locations
Geology and Formation

Chalcedony, including yellow chalcedony, is a type of microcrystalline quartz that forms in a variety of geological environments. The primary component of chalcedony is silica (SiO2), the same mineral that makes up quartz crystals. However, unlike macrocrystalline quartz, which has larger and visible crystals, chalcedony is composed of microscopic crystals.
Formation Process:
The formation of chalcedony involves the precipitation of silica from solutions, often in cavities within rocks. This process occurs at relatively low temperatures and pressures compared to the formation of larger quartz crystals. Chalcedony can form in various host rocks, including sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks. The presence of silica-rich fluids, often associated with hydrothermal activity or groundwater percolation, contributes to the formation of chalcedony.
In cavities or voids within rocks, silica-rich solutions infiltrate the space, and over time, microscopic crystals of chalcedony grow, creating a compact and fine-grained texture. The distinctive waxy luster of chalcedony is a result of its microcrystalline structure.
Mineral Composition:
The mineral composition of chalcedony is primarily silicon dioxide (SiO2). In addition to silica, chalcedony may contain various impurities and trace elements that give rise to its diverse colors. In the case of yellow chalcedony, the coloration is often attributed to the presence of iron oxides or other minerals.
Occurrence and Mining Locations:
Chalcedony is a widespread gemstone and is found on every continent. Its occurrence is diverse, and it can be associated with various geological settings:
- Volcanic Rocks: Chalcedony can form in the vesicles (gas bubbles) of volcanic rocks. This includes rocks like basalt, where cavities are filled with silica-rich solutions.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Chalcedony can also be found in sedimentary rocks, often filling voids in limestone or shale.
- Hydrothermal Deposits: In hydrothermal systems, where hot fluids circulate through the Earth’s crust, chalcedony can precipitate from silica-rich solutions.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Chalcedony can form in certain metamorphic environments, particularly those with silica-rich fluids.
Mining locations for chalcedony, including yellow chalcedony, vary depending on the type and color of the gemstone. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, the United States, Madagascar, and India are known for producing chalcedony in various colors. Mining operations involve extracting the gemstone from host rocks, and the material is then processed and cut for use in jewelry and ornamental objects.
Physical Properties

The physical properties of yellow chalcedony, like any other variety of chalcedony, are influenced by its mineral composition and structural characteristics. Here are some key physical properties of yellow chalcedony:
- Color: As the name suggests, yellow chalcedony exhibits various shades of yellow. The color can range from pale and subtle yellows to deeper, more saturated tones. The presence of iron impurities is often responsible for the yellow coloration.
- Luster: Chalcedony, including yellow chalcedony, typically displays a waxy or vitreous luster. The surface of the gemstone reflects light in a way that gives it a smooth and somewhat glossy appearance.
- Transparency: Yellow chalcedony is usually translucent, allowing some light to pass through but not as much as in transparent gemstones. This property contributes to the gemstone’s attractive visual appeal.
- Hardness: Chalcedony has a hardness of 6.5 to 7 on the Mohs scale. While it is not as hard as some gemstones like diamonds, it is still relatively durable, making it suitable for use in jewelry.
- Crystal System: Chalcedony belongs to the trigonal crystal system. Its crystals are microcrystalline and often too small to be seen with the naked eye. The lack of visible crystals contributes to its smooth and even appearance.
- Cleavage and Fracture: Chalcedony does not exhibit cleavage, and its fracture is typically conchoidal. This means that if the gemstone is broken or chipped, the resulting fragments have smooth, curved surfaces.
- Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of chalcedony ranges from approximately 2.58 to 2.64. Specific gravity is a measure of a mineral’s density compared to the density of water.
- Streak: The streak of yellow chalcedony is white, as is the case with most varieties of chalcedony.
These physical properties collectively contribute to the gemstone’s overall appearance, durability, and suitability for various jewelry applications. Jewelers and gem enthusiasts consider these properties when assessing and working with yellow chalcedony.
Applications and Uses

Yellow chalcedony, like other varieties of chalcedony, finds diverse applications and uses due to its attractive appearance, durability, and versatility. Here are some common applications:
- Jewelry:
- Gemstone Settings: Yellow chalcedony is often used in various types of jewelry settings, including rings, earrings, pendants, and bracelets. Its vibrant yellow color can complement a wide range of metal settings, making it a popular choice for fashion jewelry.
- Beads and Cabochons: The gemstone is frequently carved into beads and cabochons for use in necklaces and other beadwork. Its smooth and translucent surface makes it suitable for intricate carvings.
- Ornamental Objects:
- Carvings and Sculptures: Chalcedony, including yellow chalcedony, is appreciated for its suitability for carving. Artisans create intricate sculptures, figurines, and ornamental objects from this gemstone.
- Cameos: Chalcedony has a long history of being used for carving cameos. The layers and colors within the gemstone allow artists to create detailed and contrasting designs.
- Metaphysical and Healing:
- Metaphysical Beliefs: In various metaphysical and spiritual practices, yellow chalcedony is believed to have positive effects on emotional balance, confidence, and creativity. It is often associated with attributes such as warmth, joy, and vitality.
- Healing Properties: Some individuals believe that yellow chalcedony possesses healing properties and can promote physical well-being. It is said to stimulate the solar plexus chakra, which is associated with personal power and confidence.
- Home Decor:
- Decorative Objects: Yellow chalcedony may be used in decorative objects such as vases, bowls, and tabletop items. Its appealing color can add a touch of elegance to interior spaces.
- Collector’s Items:
- Gemstone Collections: Given its variety of colors and patterns, chalcedony, including the yellow variety, is sought after by gemstone collectors. Unique and rare specimens may be collected for their aesthetic and geological significance.
- Lapidary Arts:
- Cabochon Cutting: Lapidarists often cut yellow chalcedony into cabochons, taking advantage of its translucent quality. These cabochons can be incorporated into a variety of jewelry designs.
- Fashion Accessories:
- Accessories: Yellow chalcedony may be used in the creation of fashion accessories such as brooches, hairpins, and cufflinks, adding a pop of color to various items.
When using yellow chalcedony, designers and artisans capitalize on its unique properties to create aesthetically pleasing and meaningful pieces for a wide range of applications. The gemstone’s versatility allows it to be appreciated in both traditional and contemporary contexts.
Mining Locations

Yellow chalcedony, like various other chalcedony varieties, can be found in different parts of the world. Mining locations vary, and the gemstone is often associated with specific geological formations. Here are some notable mining locations for yellow chalcedony:
- Brazil:
- Brazil is a significant source of chalcedony, including yellow chalcedony. The gemstone is found in various regions throughout the country, and Brazilian chalcedony is known for its vibrant colors.
- Mexico:
- Mexico is another country where chalcedony, in different colors including yellow, is mined. Deposits can be found in various states, and Mexican chalcedony is appreciated for its quality and variety.
- United States:
- The United States has several locations known for chalcedony deposits. States like Oregon, California, and Arizona are recognized for producing various colors of chalcedony, including yellow. The nodules and geodes found in these areas often contain chalcedony.
- Madagascar:
- Madagascar is a known source of gem-quality chalcedony, and yellow chalcedony can be found in the country. Madagascar is renowned for its diverse gemstone deposits.
- India:
- India has a rich history of gemstone mining, and chalcedony, including yellow varieties, is found in different regions. Indian chalcedony is often used in traditional jewelry.
- Namibia:
- Namibia is recognized for its gemstone deposits, and chalcedony is among the minerals extracted. The country is known for producing chalcedony in various colors, including yellow and blue.
- Australia:
- Chalcedony deposits can be found in different parts of Australia. The gemstone is often associated with agate nodules and can be sourced from various regions across the continent.
It’s important to note that chalcedony can occur in a wide range of geological settings, including volcanic rocks, sedimentary rocks, and hydrothermal deposits. Gemstone mining operations involve extracting the material from host rocks, processing it, and preparing it for use in various applications, such as jewelry and ornamental objects.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!