Suleiman Agate
Suleiman Agate, also known as Sulemani Agate or Sulemani Hakik, is a type of agate stone that is primarily found in India. It is named after the great Ottoman Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, as it was believed to have been his favorite gemstone.

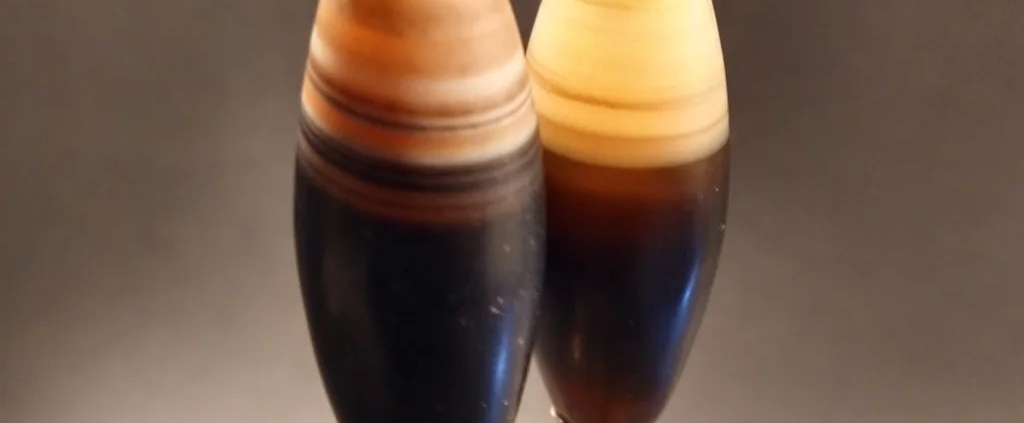
This variety of agate is characterized by its predominantly black or dark brown color with white or grayish bands or stripes running through it. These bands are often irregular and can create intricate and unique patterns within the stone. Suleiman Agate is a form of chalcedony, which is a type of cryptocrystalline quartz, and it is typically found in volcanic rocks or as nodules in sedimentary deposits.
Historically, Suleiman Agate has been highly regarded in various cultures for its believed metaphysical properties. In Islamic tradition, it is considered to have protective qualities and is often worn as an amulet or talisman to ward off negative energy and bring good luck. It is also associated with grounding, stability, and emotional balance.

Furthermore, Suleiman Agate has been valued for its aesthetic appeal and has been used in jewelry and ornamental objects for centuries. Its striking contrast of colors and intricate patterns make it a sought-after gemstone for both collectors and jewelry enthusiasts.
In summary, Suleiman Agate is a type of agate stone known for its black or dark brown coloration with white or grayish bands. It holds historical significance as a gemstone associated with protection and good fortune, particularly in Islamic tradition, and is prized for its beauty and unique patterns.
Contents
- Formation and Composition
- Physical Characteristics
- Geographic Distribution
- Uses and Applications
Formation and Composition

Suleiman Agate, like other agate varieties, is formed through a combination of volcanic and sedimentary processes over long periods of time. Here’s a breakdown of its formation and composition:
- Formation: Agates typically form in cavities within volcanic rocks, such as basalt. These cavities, known as vesicles, are created by gas bubbles trapped in the lava during its solidification. Over time, groundwater rich in silica seeps into these cavities, depositing layers of silica-rich material. This process occurs over thousands to millions of years, with successive layers of silica forming the characteristic bands or stripes seen in agate stones.
- Composition: Suleiman Agate, like all agates, is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), which is the chemical compound for quartz. However, what distinguishes agates from other forms of quartz is their microcrystalline structure. This means that the quartz crystals within agate are extremely small and tightly packed together, giving it a smooth and uniform appearance.
- Coloration and Banding: The coloration and banding in Suleiman Agate are the result of impurities and trace elements present during its formation. The dark background color, typically black or dark brown, is due to the presence of iron and manganese oxides. The contrasting bands or stripes, often white, gray, or other earthy tones, are caused by variations in mineral content or changes in environmental conditions during the agate’s formation. These bands can vary in thickness, color intensity, and arrangement, resulting in the unique patterns characteristic of Suleiman Agate.
- Inclusions and Other Features: Suleiman Agate may also contain other mineral inclusions, such as dendritic patterns (fern-like formations), mineral nodules, or even fossilized remains. These inclusions add to the stone’s visual interest and can provide clues about the geological history of the region where the agate formed.
Overall, Suleiman Agate’s formation and composition reflect a complex interplay of geological processes and environmental factors, resulting in a visually stunning and highly prized gemstone.
Physical Characteristics

Suleiman Agate possesses several physical characteristics that distinguish it as a unique and desirable gemstone. Here are some key physical characteristics:
- Color: Suleiman Agate typically exhibits a dark background color, ranging from black to dark brown. This dark hue is often interspersed with contrasting bands or stripes in white, gray, or earthy tones. The exact coloration can vary widely depending on the specific mineral impurities present during its formation.
- Transparency: Suleiman Agate is generally translucent to opaque, meaning that light can pass through it to some extent, but it is not completely transparent. The level of transparency can vary depending on the thickness of the stone and the presence of impurities or inclusions.
- Luster: Agate, including Suleiman Agate, typically exhibits a vitreous or glassy luster when polished. This luster enhances the stone’s visual appeal and gives it a smooth, glossy appearance.
- Hardness: Suleiman Agate has a hardness of approximately 6.5 to 7 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively durable and suitable for use in jewelry and ornamental objects. However, it is still susceptible to scratching and chipping, particularly if subjected to rough handling or contact with harder materials.
- Texture: When polished, Suleiman Agate has a smooth and sometimes waxy texture. This texture enhances the stone’s tactile appeal and contributes to its overall aesthetic quality.
- Pattern: One of the most distinctive physical characteristics of Suleiman Agate is its banding or striping pattern. These bands can vary in thickness, color intensity, and arrangement, creating visually captivating and intricate patterns within the stone. The patterns are often irregular and unique to each individual specimen, making each piece of Suleiman Agate truly one-of-a-kind.
Overall, Suleiman Agate’s physical characteristics combine to create a gemstone that is not only visually stunning but also durable and versatile, suitable for a wide range of jewelry and decorative applications.
Geographic Distribution

Suleiman Agate is primarily found in India, particularly in the western states of Gujarat and Maharashtra. These regions are known for their rich deposits of agate and other gemstones, which have been mined for centuries.
Within India, specific areas known for producing Suleiman Agate include:
- Khambhat (also known as Cambay): Located in the state of Gujarat, Khambhat is one of the major centers for agate mining and processing in India. The city has a long history of agate trade and is renowned for its high-quality Suleiman Agate and other varieties of agate stones.
- Jalgaon: Situated in the state of Maharashtra, Jalgaon is another significant region for agate mining and production. The area around Jalgaon is known for its diverse agate deposits, including Suleiman Agate, which is mined and processed for use in jewelry and ornamental objects.
These regions benefit from favorable geological conditions that support the formation of agate deposits, including volcanic activity and sedimentary processes. The agate-bearing rocks are often found in riverbeds, alluvial deposits, and basaltic lava flows.
While India is the primary source of Suleiman Agate, similar agate varieties may also be found in other countries with suitable geological conditions, such as Brazil, Uruguay, Madagascar, and Australia. However, Suleiman Agate specifically is most closely associated with the Indian subcontinent, where it has been mined and valued for its unique beauty and metaphysical properties for centuries.
Uses and Applications

Suleiman Agate, like other varieties of agate, is valued for its beauty, durability, and perceived metaphysical properties, leading to various uses and applications. Here are some common uses and applications of Suleiman Agate:
- Jewelry: One of the primary uses of Suleiman Agate is in jewelry making. The unique banding patterns and rich coloration of Suleiman Agate make it a popular choice for pendants, earrings, rings, bracelets, and other accessories. It can be cut and polished into various shapes and sizes to create stunning jewelry pieces that showcase its natural beauty.
- Talismans and Amulets: Suleiman Agate has a long history of being used as a talisman or amulet in various cultures, particularly in Islamic tradition. It is believed to possess protective properties and is often worn as a charm to ward off negative energy, evil spirits, and the evil eye. Many people also believe that Suleiman Agate brings good luck, stability, and emotional balance to the wearer.
- Ornamental Objects: Beyond jewelry, Suleiman Agate is also used to create ornamental objects and decorative items. These may include sculptures, figurines, paperweights, bookends, and other decorative pieces for home or office settings. The intricate patterns and rich colors of Suleiman Agate add a touch of elegance and sophistication to any space.
- Healing and Metaphysical Practices: In alternative healing and metaphysical practices, Suleiman Agate is believed to have various therapeutic properties. It is thought to promote physical strength, vitality, and stamina, as well as mental clarity, concentration, and emotional stability. Some practitioners use Suleiman Agate for crystal healing, meditation, and chakra balancing.
- Collectibles and Specimens: Collectors of gemstones and minerals may also seek out Suleiman Agate for its rarity, beauty, and unique characteristics. Specimens of Suleiman Agate with particularly striking patterns or colors may be highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts.
Overall, Suleiman Agate finds diverse uses and applications ranging from decorative and ornamental purposes to spiritual and healing practices. Its versatility, combined with its aesthetic appeal and perceived metaphysical properties, makes it a valued gemstone in various cultural contexts around the world.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!