Sepiolite
Sepiolite, also known as meerschaum, is a clay mineral that belongs to the group of phyllosilicates. It is named after the Greek word “sepion,” which means “cuttlefish bone,” due to its resemblance to the internal skeleton of cuttlefish.

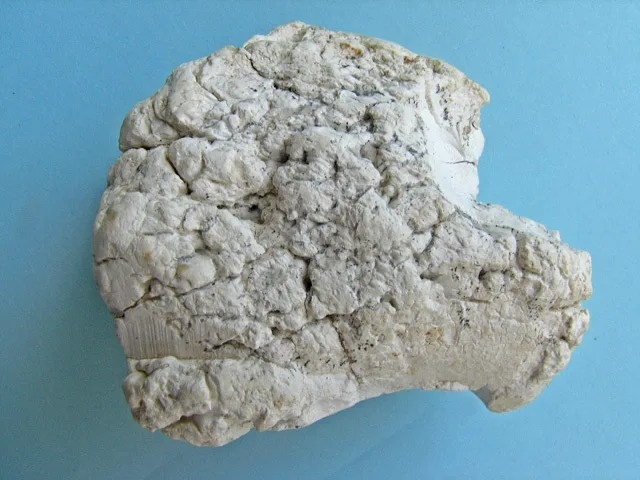

Sepiolite is primarily composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg4Si6O15(OH)2·6H2O. It forms in hydrothermal environments through the alteration of magnesium-rich rocks, such as serpentine. The mineral can occur in various colors, including white, gray, yellow, and pink, depending on impurities present in the environment during its formation.
One of the distinctive features of sepiolite is its fibrous or needle-like crystal structure. These crystals interlock to create a three-dimensional network, resulting in a unique porous structure. The pores in sepiolite give it a high surface area and exceptional absorbent properties.
Sepiolite has been used for centuries for various purposes. In the past, it was primarily known for its use in pipe making and carvings due to its soft and easily workable nature. The porous structure of sepiolite allows it to absorb water, making it useful as a filter or absorbent material. It has been employed in applications such as cat litter, oil spill cleanup, and as a desiccant to control moisture in different environments.
Furthermore, sepiolite finds applications in industries such as agriculture, construction, ceramics, and plastics. It is used as an additive in paints, coatings, and polymers to improve their properties. Sepiolite is also utilized in drilling fluids, foundry molds, and as a soil conditioner in agriculture.
Its thermal stability makes sepiolite suitable for applications requiring resistance to high temperatures. In addition, its adsorbent properties enable its use in filtration systems, water treatment, and purification processes to remove impurities and contaminants from liquids or gases.
Overall, sepiolite’s unique fibrous structure, absorbency, and versatility make it a valuable mineral with diverse applications in various industries.
Contents
- Formation and Occurrence
- Mineralogy and Physical Properties
- Geological Setting and Depositional Environment
- Associated Minerals and Rock Units
- Economic Significance and Uses
- FAQ
Formation and Occurrence
Sepiolite forms through the hydrothermal alteration of magnesium-rich rocks, particularly serpentine, under specific geological conditions. The alteration process occurs when hot water, rich in magnesium and other elements, interacts with the primary minerals present in the rocks. The exact mechanisms of sepiolite formation are still subject to ongoing scientific research and understanding.
Sepiolite is commonly found in sedimentary environments, often associated with marine deposits and alkaline lakes. It occurs in regions where there has been a combination of magnesium-rich parent rocks, hydrothermal activity, and the presence of water necessary for mineral alteration.
Some notable occurrences of sepiolite include:
- Turkey: The country is renowned for its high-quality sepiolite deposits, particularly in the Eskisehir region. The town of Sarıcakaya in Eskisehir is well-known for its sepiolite mines and has been a major source of the mineral for centuries.
- Spain: Sepiolite deposits are found in several areas of Spain, such as the province of Zaragoza, the region of Catalonia, and the Almería province. The town of Cabezo de Torres in Murcia is known for its sepiolite mines as well.
- United States: Sepiolite deposits can be found in various locations across the United States, including California, Nevada, Utah, and Arizona. The largest known sepiolite mine in the U.S. is located in Lander County, Nevada.
- Other countries: Sepiolite is also found in countries like Greece, Iran, China, Russia, Mexico, and South Africa, among others. Each location may have unique geological and environmental conditions that contribute to the formation and occurrence of sepiolite.
It’s important to note that the availability and quality of sepiolite deposits can vary in different regions. Geological surveys and assessments are conducted to identify and evaluate sepiolite resources, considering factors such as mineral purity, quantity, accessibility, and economic viability.
Overall, sepiolite is a relatively rare mineral that occurs in specific geological settings where the necessary conditions for its formation are met. Its occurrences are typically associated with magnesium-rich rocks and environments conducive to hydrothermal alteration processes.
Mineralogy and Physical Properties
Sepiolite is a clay mineral with a unique mineralogy and set of physical properties. Here are some key characteristics:
- Mineralogy: Sepiolite belongs to the group of phyllosilicate minerals. Its chemical formula is Mg4Si6O15(OH)2·6H2O, indicating its composition of hydrated magnesium silicate. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and forms fibrous or needle-like crystals that interlock to create a three-dimensional network.
- Color and Appearance: Sepiolite is typically white, gray, yellow, or pink, although it can also occur in other colors depending on impurities present during its formation. Its fibrous crystals give it a soft and chalky appearance. Sepiolite’s porous structure makes it lightweight, and it can have a frothy or porous texture, resembling sea foam or coral.
- Hardness: Sepiolite has a Mohs hardness of 2, which means it is relatively soft. It can be easily scratched or carved with a fingernail or a knife.
- Density: Sepiolite has a low density, typically ranging from 1.9 to 2.2 grams per cubic centimeter. Its lightweight nature contributes to its use in applications where weight is a factor.
- Porosity and Surface Area: One of the notable properties of sepiolite is its high porosity. The fibrous crystals create a network of pores, resulting in a high surface area. This porosity contributes to sepiolite’s absorbent and adsorbent properties, allowing it to retain liquids or adsorb impurities.
- Thermal Stability: Sepiolite exhibits good thermal stability. It can withstand high temperatures without significant changes in its structure or properties. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications that require heat resistance, such as refractory materials or insulation.
- Water Absorption: Sepiolite has excellent absorbent properties, especially for water. Its porous structure enables it to absorb and retain water within its interconnecting channels. This property makes sepiolite useful in applications like cat litter or as a desiccant for moisture control.
- Rheological Properties: Sepiolite can impart thixotropic and suspension properties to fluids. When mixed with liquids, it can act as a thickening agent, providing stability and preventing settling. This property finds applications in various industries, including paints, coatings, and drilling fluids.
These physical properties make sepiolite a unique and versatile mineral with applications ranging from absorbents and adsorbents to construction materials and additives in various industries.
Geological Setting and Depositional Environment
The geological setting and depositional environment of sepiolite can vary depending on the specific region and circumstances of its formation. However, there are some common features associated with the occurrence of sepiolite deposits.
- Hydrothermal Alteration: Sepiolite is typically formed through hydrothermal alteration processes. This involves the interaction of hot water with magnesium-rich rocks, such as serpentine, under specific temperature and pressure conditions. Hydrothermal fluids carrying dissolved magnesium and other elements infiltrate the parent rocks and initiate chemical reactions that transform the original minerals into sepiolite.
- Sedimentary Environments: Sepiolite is commonly found in sedimentary environments. It often occurs in marine deposits, including shallow marine basins, lagoons, and restricted marine environments. The presence of marine sediments suggests a connection to ancient seas or coastal areas where sepiolite deposition took place.
- Evaporitic Conditions: Sepiolite can be associated with evaporitic conditions. In regions with arid or semi-arid climates, evaporation of water in closed basins or saline lakes leads to the precipitation of salts and minerals, including sepiolite. The concentration of dissolved magnesium in the brines promotes the formation of sepiolite as the water evaporates.
- Alkaline Lakes and Saline Playas: Sepiolite is often found in alkaline lakes and saline playas (dry lake beds). These environments provide the necessary chemical conditions and evaporation processes for sepiolite deposition. The alkaline nature of the waters, along with the availability of magnesium-rich sources, contributes to the formation of sepiolite deposits.
- Tectonic and Volcanic Activity: The presence of tectonic and volcanic activity in an area can influence the formation of sepiolite deposits. Hydrothermal fluids associated with volcanic activity can carry the necessary elements for sepiolite formation and deposition. Additionally, tectonic processes, such as faulting or fracturing, can create pathways for hydrothermal fluids to infiltrate the rocks and initiate alteration.
It’s important to note that the specific geological setting and depositional environment can vary from region to region. The formation of sepiolite is influenced by a combination of factors, including the availability of magnesium-rich rocks, hydrothermal activity, evaporation processes, and local geological and climatic conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for the exploration and exploitation of sepiolite deposits.
Associated Minerals and Rock Units
Sepiolite can be associated with certain minerals and rock units based on the geological conditions in which it forms. While the specific associations may vary depending on the location, here are some minerals and rock units commonly found in conjunction with sepiolite:
- Serpentine: Sepiolite often forms through the alteration of magnesium-rich rocks, particularly serpentine. Serpentine minerals, such as antigorite or lizardite, are commonly found alongside sepiolite. These minerals serve as the precursor rocks that undergo hydrothermal alteration, leading to the formation of sepiolite.
- Magnesite: Magnesite, a mineral composed of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), can occur alongside sepiolite deposits. Both sepiolite and magnesite can be formed under similar hydrothermal conditions and may be found together in certain geological settings.
- Clay Minerals: Other clay minerals, such as smectite or kaolinite, can sometimes be associated with sepiolite deposits. These clay minerals may occur as secondary minerals formed through different alteration processes or alongside sepiolite in sedimentary sequences.
- Dolomite and Carbonate Minerals: In some instances, sepiolite deposits can occur in association with dolomite, calcite, or other carbonate minerals. These carbonate minerals may be present due to the presence of marine sediments or evaporitic conditions in the depositional environment.
- Evaporite Minerals: Sepiolite can occur in evaporitic environments alongside other evaporite minerals such as halite (rock salt), gypsum, or anhydrite. These minerals precipitate as a result of the evaporation of water in closed basins or saline lakes.
- Volcanic Rocks: In areas associated with volcanic activity, sepiolite deposits may occur in proximity to volcanic rocks such as basalt or andesite. Hydrothermal fluids carrying the necessary elements for sepiolite formation can be sourced from volcanic activity.
It’s important to note that the specific mineral associations with sepiolite can vary based on regional geological conditions. The geological setting, depositional environment, and the availability of precursor rocks and hydrothermal fluids play significant roles in determining the mineral assemblages found alongside sepiolite deposits.
Economic Significance and Uses
Sepiolite has several economic significances and finds applications across various industries. Here are some of the major uses of sepiolite:
- Absorbents and Desiccants: Sepiolite’s exceptional absorbent properties make it valuable for applications such as cat litter, oil spill cleanup, and moisture control. Its porous structure allows it to absorb and retain liquids, including water, oils, and chemicals.
- Filtration and Purification: Sepiolite is utilized in filtration systems and water treatment processes. Its high surface area and adsorbent properties enable it to effectively remove impurities, contaminants, and heavy metals from liquids and gases.
- Construction Materials: Sepiolite is used in construction and building materials. It can be incorporated into products such as cement, mortars, and plasters to improve their workability, strength, and resistance to cracking. Sepiolite’s thermal stability also makes it suitable for insulation materials and fire-resistant products.
- Rheological Additive: Sepiolite acts as a rheological additive in various industries. It imparts thixotropic properties to fluids, preventing settling and providing stability. This characteristic is valuable in applications like paints, coatings, adhesives, drilling fluids, and personal care products.
- Agriculture and Horticulture: Sepiolite is used in agriculture as a soil conditioner to improve water retention, aeration, and nutrient availability in the soil. It can also enhance the growth and yield of crops. In horticulture, sepiolite is employed in potting soils and substrates for its water-retaining properties.
- Ceramics and Refractories: Sepiolite is added to ceramics and refractory materials to enhance their properties. It can improve the plasticity and workability of clay bodies, increase thermal shock resistance, and act as a binder or fluxing agent in high-temperature applications.
- Cosmetic and Personal Care Products: Sepiolite is used in cosmetics and personal care products such as facial masks, body scrubs, and bath products. Its absorbent and exfoliating properties make it useful for removing impurities and dead skin cells, providing a gentle cleansing and exfoliating experience.
- Drilling Fluids: Sepiolite is utilized in the oil and gas industry as an additive in drilling fluids. It helps control fluid viscosity, lubricates the drill bit, and prevents fluid loss into the formation during drilling operations.
These are just a few examples of the economic significance and diverse range of applications for sepiolite. Its unique properties make it a valuable mineral in various industries, offering solutions for absorbency, filtration, construction, agriculture, cosmetics, and more.
FAQ
- What is sepiolite?
- Sepiolite is a clay mineral belonging to the group of phyllosilicates. It is composed of hydrated magnesium silicate and is known for its fibrous crystal structure and high absorbent properties.
- Where is sepiolite found?
- Sepiolite is found in various locations worldwide. Some notable sources include Turkey, Spain, the United States, Greece, Iran, China, Russia, Mexico, and South Africa.
- What are the uses of sepiolite?
- Sepiolite has diverse applications. It is used as an absorbent in cat litter and oil spill cleanup, in water filtration and purification, as a rheological additive in paints and coatings, as a soil conditioner in agriculture, in construction materials, and in various industries such as ceramics, cosmetics, and drilling fluids.
- How is sepiolite formed?
- Sepiolite forms through the hydrothermal alteration of magnesium-rich rocks, particularly serpentine. Hot water interacts with the minerals in the rocks, leading to chemical reactions that transform them into sepiolite.
- What are the physical properties of sepiolite?
- Sepiolite is a soft mineral with a fibrous crystal structure. It has a low density, high porosity, and excellent absorbent properties. Sepiolite is lightweight, has a chalky appearance, and is typically white, gray, yellow, or pink in color.
- Is sepiolite harmful to health?
- Sepiolite is generally considered safe for use in various applications. However, like any mineral dust, inhalation of fine particles may cause respiratory irritation. Proper precautions and safety measures should be followed when handling and processing sepiolite.
- Can sepiolite be used in environmental remediation?
- Yes, sepiolite is commonly used in environmental remediation processes. Its absorbent properties make it effective in absorbing and removing contaminants from soil, water, and air, aiding in the cleanup of pollutants and spills.
- Is sepiolite a renewable resource?
- Sepiolite is a naturally occurring mineral and is not considered a renewable resource. However, responsible mining practices and resource management can help ensure sustainable extraction and utilization.
- Can sepiolite withstand high temperatures?
- Yes, sepiolite exhibits good thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures without significant changes in its structure or properties. This makes it suitable for applications requiring heat resistance, such as refractory materials and insulation.
- Can sepiolite be recycled or reused?
- Sepiolite can be recycled or reused in certain applications. For example, used sepiolite cat litter can be composted or used as a soil amendment. In other industries, sepiolite may be recycled or reused depending on the specific requirements and feasibility of the process.
Please note that while these answers provide general information, specific details and considerations may vary based on the context and location of sepiolite use.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!