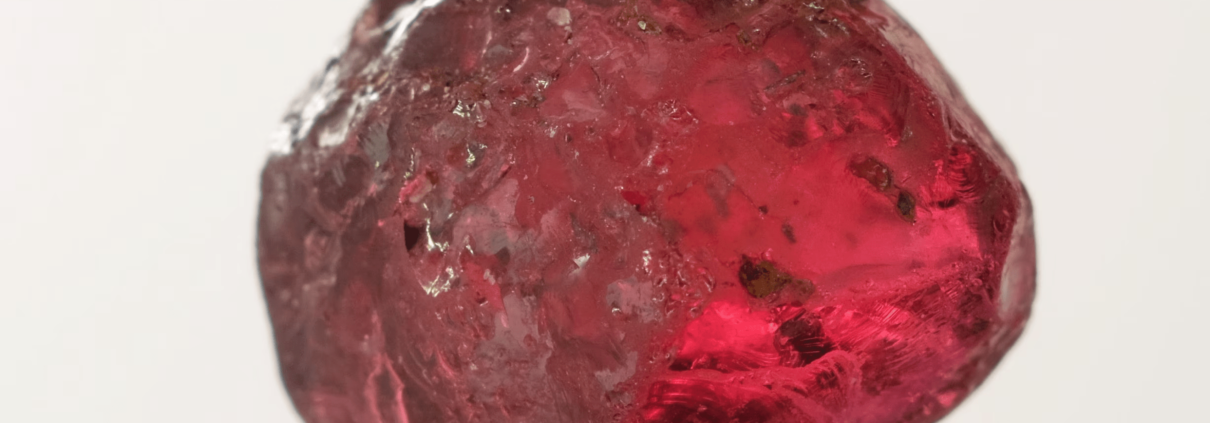
Rhodolite
Rhodolite is a gemstone that belongs to the garnet family, known for its vibrant and beautiful colors. It is a hybrid variety of garnet that combines pyrope and almandine, two of the six main types of garnets. The name “rhodolite” is derived from the Greek words “rhodon,” meaning rose, and “lithos,” meaning stone, referring to its often pinkish or reddish-purple hues.

Rhodolite typically ranges in color from a pinkish-red to a purplish-red or even a raspberry-red tone. Its colors are often reminiscent of the lush red and pink shades found in rose petals, making it a highly sought-after gemstone for jewelry.
This gemstone is transparent and exhibits excellent brilliance and sparkle, making it a favorite choice for various types of jewelry, including rings, earrings, necklaces, and pendants. Its hardness on the Mohs scale falls between 7 and 7.5, making it durable and suitable for everyday wear.
Significance: Rhodolite has gained popularity not only for its stunning appearance but also for its symbolism and metaphysical properties. It is believed to have several beneficial qualities:
- Emotional Balance: Rhodolite is said to promote emotional healing and balance. It is believed to encourage love, compassion, and self-acceptance, helping individuals overcome emotional scars and traumas.
- Creativity: Some people believe that rhodolite can stimulate creativity and inspire artistic expression.
- Protection: In folklore, garnets in general, including rhodolite, are thought to provide protection from negative energies and enhance one’s sense of security.
- Strength: Rhodolite is associated with strength and vitality, helping wearers feel more energized and confident.

Popularity and Demand: Rhodolite garnets have gained popularity in recent years due to their attractive colors and affordability compared to some other gemstones. Here are some factors contributing to their popularity and demand:
- Color Variety: Rhodolite’s range of colors, from pinkish-red to purplish-red, offers versatility for jewelry designers and allows individuals to find the shade that resonates with them.
- Affordability: Rhodolite is often more affordable than other red or pink gemstones like ruby or pink sapphire, making it an attractive option for those seeking a similar look without the high price tag.
- Durability: With a hardness of 7 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, rhodolite is sufficiently durable for everyday wear in various jewelry settings.
- Unique Appearance: The unique blend of red and purple hues in rhodolite sets it apart from other gemstones, giving it a distinct and eye-catching appearance.
- Metaphysical Appeal: Some individuals are drawn to rhodolite for its perceived metaphysical properties and healing attributes.
Overall, the combination of its aesthetic appeal, affordability, and symbolism has contributed to the growing popularity and demand for rhodolite gemstones in the jewelry market.
Contents
- Characteristics of Rhodolite
- Rhodolite’s Geological Background
- Rhodolite Uses
Characteristics of Rhodolite

- Color: Rhodolite is known for its stunning range of colors, which typically fall into the pinkish-red to purplish-red spectrum. These colors can resemble the hues of rose petals, raspberries, or even cranberries. The precise coloration may vary, but it should have a vibrant and attractive appearance.
- Transparency: Rhodolite is a transparent gemstone, allowing light to pass through it. This transparency contributes to its sparkle and brilliance.
- Luster: Rhodolite exhibits a vitreous or glassy luster, which adds to its overall attractiveness.
- Hardness: Rhodolite garnets have a hardness ranging from 7 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making them suitable for use in various types of jewelry, including rings, earrings, and necklaces.
- Clarity: While most rhodolite gemstones are relatively free of visible inclusions, they can occasionally have some minor flaws or natural inclusions. High-quality rhodolites are typically eye-clean, meaning that inclusions are not visible to the naked eye.
- Cut: Rhodolite is often cut into various shapes, including rounds, ovals, cushions, and pear shapes, to maximize its brilliance and color display. Precision cutting can enhance its overall appearance.
- Carat Weight: Rhodolite garnets can be found in a range of carat weights, from small accent stones to larger centerpieces. Larger stones with excellent color and clarity are particularly prized.
- Origin: Rhodolite garnets can be found in various locations around the world, including Sri Lanka, Brazil, India, Mozambique, Tanzania, and the United States (North Carolina). The origin can sometimes affect the gem’s color and value, with some regions known for producing particularly vibrant stones.
- Fluorescence: Rhodolite garnets may exhibit weak to moderate fluorescence when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This property can vary among individual stones and may not significantly impact their appearance.
- Treatment: In most cases, rhodolite garnets are not treated with heat or other enhancements. Their natural colors and characteristics are highly valued in their unaltered state.
- Setting: Rhodolite gemstones are versatile and can be set in various types of jewelry settings, from classic solitaire rings to elaborate pendant designs. They are often paired with white or yellow gold, as well as other gemstones, to create unique and attractive jewelry pieces.
In summary, rhodolite is a gemstone prized for its vibrant colors, transparency, durability, and versatility. Its unique combination of characteristics makes it a popular choice for jewelry designers and enthusiasts alike.
Rhodolite’s Geological Background

Formation Process: Rhodolite is a variety of garnet and shares its formation process with other members of the garnet group. Garnets are typically formed in metamorphic rocks, which are rocks that have undergone significant heat and pressure deep within the Earth’s crust. The formation of rhodolite involves the following key processes:
- Metamorphism: Garnets, including rhodolite, begin their formation within existing rocks like schist, gneiss, or mica-rich rocks. These parent rocks are subjected to intense heat and pressure during metamorphism, causing minerals within them to recrystallize and rearrange.
- Hydrothermal Fluids: During metamorphism, hot, mineral-rich fluids are often present. These hydrothermal fluids carry elements like aluminum, silicon, and oxygen, which are essential for garnet formation.
- Chemical Reactions: The chemical reactions between the mineral constituents of the parent rock and the infiltrating hydrothermal fluids lead to the growth of garnet crystals over time.
- Composition: Rhodolite specifically forms when the garnet crystal incorporates a balanced mixture of pyrope (Mg3Al2Si3O12) and almandine (Fe3Al2Si3O12) compositions. This combination gives rhodolite its characteristic pinkish to purplish-red colors.
- Grain Growth: As the garnet crystals continue to grow, they develop the distinctive crystal structure and properties associated with garnets, including the transparency and hardness.

Geological Locations: Rhodolite garnets have been found in various geological locations around the world. Some notable sources include:
- Sri Lanka: Sri Lanka is known for producing high-quality rhodolite garnets with vibrant colors, often referred to as “Ceylon rhodolite.”
- Brazil: Brazilian rhodolite garnets are renowned for their rich red and pink hues.
- India: India is another significant source of rhodolite garnets, particularly in the state of Rajasthan.
- Mozambique: Mozambique has also become a notable producer of rhodolite garnets in recent years, known for its deep red and purplish-red stones.
- Tanzania: Tanzania, especially the Umba Valley region, is a source of rhodolite garnets with a range of colors, from pinkish-red to purplish-red.
- United States: North Carolina, in the United States, has produced rhodolite garnets, adding to the global supply.
Gemstone Family (Garnet Group): Rhodolite is a member of the garnet group, which is a diverse family of minerals known for their wide range of colors and varieties. The garnet group includes several other well-known gemstones, each with its unique composition and characteristics. Some notable members of the garnet family include:
- Almandine: Deep red to brownish-red garnet.
- Pyrope: Deep red to purplish-red garnet, often referred to as “ruby red.”
- Spessartite: Orange to reddish-brown garnet.
- Grossular: Various colors, including green, yellow, and colorless varieties.
- Andradite: Green to brownish-green garnet, with rare varieties like demantoid and melanite.
- Uvarovite: Bright green garnet, often found in tiny crystal grains.
Rhodolite stands out in the garnet group due to its pinkish to purplish-red colors, which make it a sought-after and distinctive variety of this diverse gemstone family.
Rhodolite Uses

Rhodolite, with its vibrant and appealing colors, durability, and versatility, is a popular gemstone used in a variety of jewelry and decorative applications. Here are some common uses of rhodolite:
- Jewelry: Rhodolite gemstones are primarily used in jewelry design. They are cut into various shapes and sizes and set in a wide range of jewelry pieces, including:
- Rings: Rhodolite is often used as the center stone in engagement rings, cocktail rings, and fashion rings.
- Earrings: Rhodolite earrings, both studs and dangle earrings, are popular for adding a touch of color and elegance to any outfit.
- Necklaces: Rhodolite pendants and necklaces can feature single or multiple stones, making them versatile for everyday wear or special occasions.
- Bracelets: Rhodolite gemstones can be set into bracelets, adding a pop of color to the wrist.
- Birthstone Jewelry: Rhodolite is considered a suitable birthstone for individuals born in January, making it a meaningful choice for personalized jewelry.
- Custom Jewelry: Jewelry designers often use rhodolite in custom-made pieces, allowing customers to create unique and personalized jewelry items.
- Mixed Gemstone Jewelry: Rhodolite can be combined with other gemstones, such as diamonds, sapphires, or emeralds, to create visually striking and colorful jewelry designs.
- Collector’s Items: Exceptional and rare rhodolite specimens may be collected by gemstone enthusiasts and collectors for their beauty and uniqueness.
- Metaphysical and Healing Jewelry: Some individuals believe in the metaphysical properties of rhodolite and use it in jewelry to promote emotional healing, balance, and positivity.
- Home Decor: While less common, rhodolite may also be used as decorative accents in home decor items such as sculptures, vases, or as inlays in furniture.
- Investment: High-quality, large rhodolite gemstones can appreciate in value over time, making them potential investments for those interested in gemstone trading and investment.
It’s important to note that the primary use of rhodolite remains in the creation of stunning jewelry pieces, where its colors and durability shine, providing wearers with a touch of elegance and sophistication. Whether used in traditional settings or more modern, avant-garde designs, rhodolite continues to captivate jewelry enthusiasts and gemstone lovers alike.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!