Purple Scapolite
Purple scapolite is a mineral that belongs to the group of aluminosilicate minerals. Scapolite is named after the Greek word “skapos,” which means “rod” or “stick,” referring to its long prismatic crystal habit. It is a relatively rare mineral, and its color can vary widely depending on the specific chemical composition. Purple scapolite is a specific color variety that distinguishes itself from other types of scapolite.
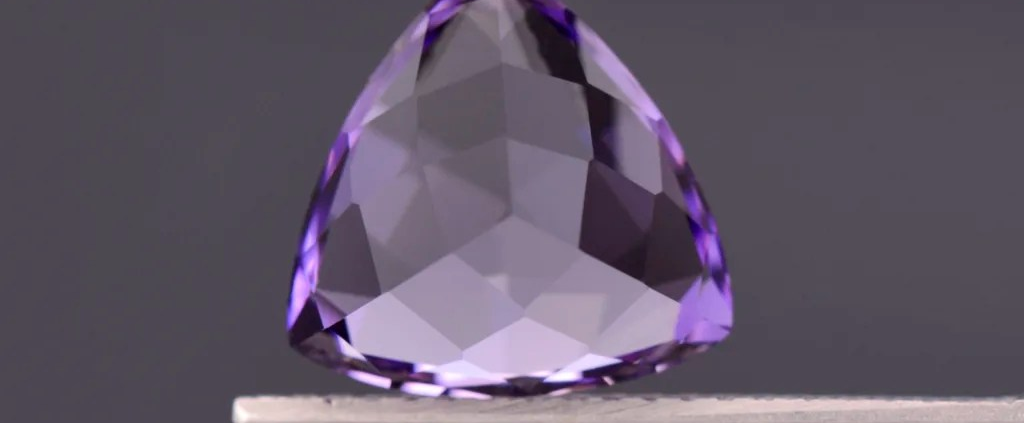
 Scapolite Gemstone from Tanzania, 3.32 cts (https://kosnargemco.com/listing/1239077352/exceptional-purple-scapolite-gemstone)
Scapolite Gemstone from Tanzania, 3.32 cts (https://kosnargemco.com/listing/1239077352/exceptional-purple-scapolite-gemstone)
Scapolite in General: Scapolite is a mineral that typically occurs in metamorphic and igneous rocks. It is composed of aluminum, silicon, oxygen, and chlorine, with additional elements like sodium and calcium. The exact chemical composition can vary, leading to different color variations.
Purple Scapolite: What sets purple scapolite apart is its distinct purple coloration. The purple hue is due to trace elements within the crystal structure, such as manganese and iron. These impurities give the mineral its vibrant violet to lavender shades. The intensity of the purple color can vary, with some specimens being quite pale and others having a deep purple hue.
Purple scapolite is valued both as a collector’s mineral and as a gemstone. Its unique color and rarity make it an attractive option for jewelry, although it is not as well-known as some other gemstones like sapphire or amethyst. When used in jewelry, purple scapolite is typically faceted to showcase its brilliance and color. It’s essential to note that like all gemstones, the quality of purple scapolite can vary, and the value is influenced by factors such as color intensity, clarity, and size.
Contents
- Physical Properties and Characteristics
- Gemological Information of Purple Scapolite
- Uses and Applications of Purple Scapolite
- Occurrence and sources of purple scapolite
Physical Properties and Characteristics

Purple scapolite, like other varieties of scapolite, possesses distinct physical properties and characteristics that help identify and differentiate it from other minerals. Here are some of its key physical properties and characteristics:
- Color: As the name suggests, the most prominent characteristic of purple scapolite is its purple to lavender color. The color can vary in intensity, ranging from pale lilac to deep violet, and is caused by trace elements, primarily manganese and iron, within the crystal structure.
- Crystal Habit: Scapolite typically forms prismatic crystals with a long, slender shape. These crystals can be well-formed and exhibit a striated or grooved texture along their length.
- Cleavage: Purple scapolite has two distinct cleavage directions, which means it can easily break along two specific planes, creating flat, smooth surfaces. The cleavage angles are not always perfect, but they contribute to its characteristic appearance.
- Hardness: Scapolite has a moderate to relatively high hardness, typically ranging from 5.5 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale. This hardness makes it suitable for use in jewelry, but it may require some care to prevent scratching.
- Luster: Purple scapolite has a vitreous to silky luster when polished. This luster gives the mineral a noticeable shine when cut and polished for use in jewelry.
- Transparency: It is typically translucent to transparent, allowing light to pass through the crystal. This property is essential for gem-quality purple scapolite.
- Density: The density of scapolite varies depending on its specific composition and can range from 2.60 to 2.75 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Chemical Composition: Purple scapolite is composed of aluminum, silicon, oxygen, and chlorine, with varying amounts of sodium, calcium, and trace elements like manganese and iron.
- Fluorescence: Some purple scapolite specimens may exhibit fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) light. The fluorescence can vary in color, typically showing bright yellow, orange, or pink fluorescence.
- Fracture: The mineral can exhibit conchoidal fracture, which means it may break with curved, shell-like patterns, especially if it doesn’t cleave cleanly.
- Twinning: Twinning, where two crystals are joined symmetrically, can occur in scapolite, affecting its overall crystal shape.
It’s important to note that the physical properties of purple scapolite can vary slightly depending on the specific locality and the presence of impurities. These characteristics collectively make purple scapolite a unique and visually appealing mineral, suitable for both mineral collectors and gem enthusiasts. When used as a gemstone, its distinctive color and luster are highlighted through faceting and polishing to create stunning jewelry pieces.
Gemological Information of Purple Scapolite

Gemological information about purple scapolite is essential for those interested in using it as a gemstone or for collectors who want to understand its quality and value. Here are some key gemological details about purple scapolite:
- Refractive Index (RI): The refractive index of purple scapolite typically falls within the range of approximately 1.540 to 1.578. This property helps gemologists identify the material and assess its optical characteristics.
- Birefringence: Purple scapolite is usually strongly birefringent. Gemologists use a refractometer to measure this property, which can aid in distinguishing it from other gemstones with similar colors.
- Dispersion: Purple scapolite has low dispersion, meaning it does not exhibit the “fire” or spectral colors seen in some other gemstones like diamond or zircon.
- Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of purple scapolite falls between 2.60 and 2.75. This measurement helps distinguish it from other gem materials with similar appearances.
- Hardness: As mentioned earlier, purple scapolite has a hardness ranging from 5.5 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale, making it suitable for use in jewelry, though care should be taken to prevent scratching.
- Luster: It displays a vitreous to silky luster, which enhances its visual appeal when cut and polished.
- Clarity: Clarity in purple scapolite can vary. Some specimens may be relatively free of visible inclusions, while others may exhibit various types of internal flaws. Gemstone quality is often assessed based on the presence and visibility of these inclusions.
- Cut: Purple scapolite is typically faceted to maximize its brilliance and color. The choice of cut can influence how well the stone showcases its purple hue.
- Color: The most critical factor in assessing the quality of purple scapolite is its color. The most valuable specimens exhibit a vibrant and saturated purple to lavender hue. The intensity, tone, and uniformity of color play a significant role in determining its value.
- Treatments: Natural purple scapolite is typically not subjected to treatments, but like many gemstones, it’s essential to inquire about any enhancements or treatments when purchasing.
- Fluorescence: Some purple scapolite specimens may fluoresce under ultraviolet (UV) light. Gemologists can use this property to help identify and authenticate the gemstone.
- Origin: The origin of a purple scapolite can impact its desirability and value. Gemstones from well-known sources like Madagascar or Tanzania may command higher prices due to their reputation for producing high-quality material.
Overall, purple scapolite is a unique and attractive gemstone with its distinct color and optical properties. When evaluating its quality and value, gemologists and buyers should pay close attention to color, clarity, and the absence of treatments, among other factors, to make informed decisions about purchasing or collecting this beautiful gemstone.
Uses and Applications of Purple Scapolite

Purple scapolite, like other gemstones and minerals, has various uses and applications, primarily in the jewelry and gemstone industry. Here are some of the main uses and applications of purple scapolite:
- Gemstone Jewelry: Purple scapolite is often cut and polished to create beautiful gemstones for use in jewelry. Its vibrant purple color and luster make it an attractive choice for various types of jewelry, including rings, earrings, pendants, and necklaces. The gemstones can be used as centerpieces or accent stones in both contemporary and traditional designs.
- Collectibles and Mineral Specimens: Many collectors are drawn to the unique color and rarity of purple scapolite. It is often sought after by mineral enthusiasts and collectors who appreciate its distinctive crystal structure and aesthetic appeal. High-quality specimens are sometimes displayed in mineral collections.
- Metaphysical and Healing Properties: Some individuals believe in the metaphysical and healing properties of gemstones, including purple scapolite. It is thought to promote inner peace, emotional balance, and spiritual growth. It may be used in crystal healing practices, meditation, and energy work.
- Ornamental Objects: Purple scapolite can be used in ornamental objects and decorative items. While not as common as its use in jewelry, it may find its way into sculptures, carvings, and other art forms.
- Birthstone and Zodiac Jewelry: Some people associate gemstones with birth months and zodiac signs. Purple scapolite, with its purple color, is sometimes used as a birthstone for individuals born in certain months or under specific zodiac signs that align with the color purple.
- Fashion Accessories: Purple scapolite gemstones can be incorporated into fashion accessories such as brooches, cufflinks, and hairpins, adding a touch of elegance and color to attire.
- Investment: In some cases, rare and high-quality purple scapolite gemstones can be considered as investments. Their value may appreciate over time, especially if they are from renowned sources and exhibit exceptional characteristics.
It’s important to note that while purple scapolite has various uses, its availability is relatively limited compared to more common gemstones like diamonds, sapphires, or emeralds. This rarity can make high-quality purple scapolite specimens and gemstones particularly valuable and desirable to collectors and jewelry enthusiasts. When purchasing purple scapolite for any purpose, it’s essential to work with reputable dealers and consider factors such as color, clarity, cut, and origin to ensure you are acquiring a genuine and valuable piece.
Occurrence and sources of purple scapolite

Purple scapolite, as a specific color variety of the scapolite mineral, is relatively rare compared to other gemstones and minerals. It can be found in various geological settings around the world, but some sources are more well-known for producing high-quality purple scapolite specimens. Here are some of the notable occurrences and sources of purple scapolite:
- Madagascar: Madagascar is perhaps the most famous source for purple scapolite. The country is known for producing high-quality specimens with rich and vibrant purple coloration. The material from Madagascar is highly sought after by gemstone enthusiasts and collectors.
- Tanzania: Purple scapolite is also found in Tanzania, often in association with other gemstones like tanzanite and sapphire. Tanzanian purple scapolite may exhibit various shades of purple and is valued for its unique coloration.
- Canada: Purple scapolite has been discovered in Canada, particularly in the province of Ontario. Canadian purple scapolite can range in color from light lavender to deep violet and is occasionally used in jewelry.
- Brazil: Brazil has been a source of scapolite, including purple varieties. While not as well-known as some other sources, Brazilian purple scapolite specimens can be found in the market.
- Myanmar (Burma): Myanmar is known for producing various gemstones, and purple scapolite has been found there as well. However, it is not a primary source, and the availability may be limited compared to other gemstones found in the region.
- Russia: Purple scapolite has also been reported in some regions of Russia, such as the Murmansk Oblast in the Kola Peninsula. Russian purple scapolite can vary in color and quality.
- Kenya: Kenya is another East African country where purple scapolite has been discovered. While not as prominent as Tanzania in terms of gemstone production, Kenyan purple scapolite can still be found.
It’s important to note that the quality and availability of purple scapolite can vary widely depending on the specific locality and the characteristics of the individual specimens. Gemstone dealers and collectors often seek out sources known for producing high-quality purple scapolite with intense and consistent coloration.
When evaluating and purchasing purple scapolite, consider factors such as color, clarity, size, and origin to determine its value and desirability. Reputable gemstone dealers and laboratories can provide certification and information about the origin and quality of the gemstone to ensure that you are acquiring an authentic and valuable piece of purple scapolite.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!