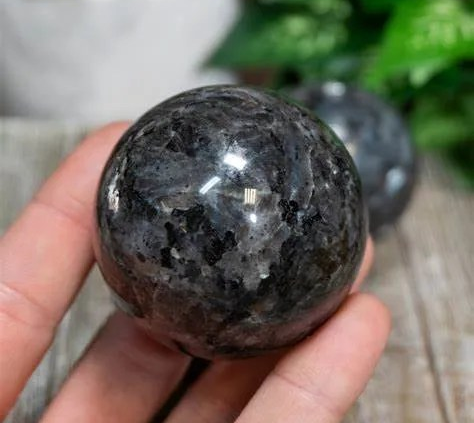
Larvikite
Larvikite is a unique and visually striking igneous rock that belongs to the family of feldspar-rich plutonic rocks known as syenites. It is primarily composed of feldspar minerals, particularly oligoclase, with additional presence of hornblende, augite, and other minor minerals. Larvikite is renowned for its distinctive blue-grey to silver-gray coloration, often adorned with iridescent blue or silver highlights caused by the presence of labradorite feldspar. This remarkable rock is celebrated for its aesthetic qualities and is frequently used in both architectural and decorative applications due to its captivating appearance.


Contents
- Geological Formation
- Geographic Distribution
- Physical Characteristics of Larvikite
- Uses of Larvikite
Geological Formation
Larvikite is formed through a complex geological process that typically occurs deep within the Earth’s crust. It is primarily associated with intrusive igneous activity. The formation of larvikite can be summarized as follows:

- Magma Generation: Larvikite begins its formation when magma, or molten rock, is generated in the Earth’s mantle. This process often involves the partial melting of pre-existing rocks, such as basaltic or gabbroic materials.
- Intrusion: The molten magma rises towards the Earth’s surface through fractures or conduits in the crust. As it ascends, it intrudes into the surrounding rocks, displacing and interacting with them.
- Cooling and Crystallization: As the magma begins to cool, the minerals within it start to crystallize. Larvikite is predominantly composed of feldspar minerals, especially oligoclase, which crystallize from the cooling magma.
- Slow Cooling: What makes larvikite particularly unique is its slow cooling rate. This slow cooling allows for the growth of larger feldspar crystals, contributing to the rock’s distinctive appearance.
- Mineral Differentiation: During the cooling process, other minerals such as hornblende and augite may also crystallize in the larvikite, adding to its mineral composition.
- Geological Time: The formation of larvikite is a slow and gradual process that can take millions of years. The rock gradually solidifies and becomes part of the Earth’s crust.
- Geological Forces: Over time, geological forces, including tectonic movements and erosion, can bring larvikite to the Earth’s surface, where it may be exposed through natural processes or extracted for various uses, including construction and decoration.
Larvikite’s distinctive appearance, characterized by its iridescent blue or silver highlights, is a result of the presence of labradorite feldspar, which exhibits a phenomenon known as “labradorescence.” This optical effect adds to the rock’s allure and makes it highly sought after in the world of architecture and design.
Geographic Distribution

Larvikite is primarily found in specific geological regions, and its geographic distribution is relatively limited. It is most notably associated with Norway, where it occurs in significant quantities and is even named after the town of Larvik in the Vestfold region. However, larvikite can also be found in a few other locations worldwide, although in smaller quantities. Here are the main geographic regions where larvikite is known to occur:
- Norway: Larvikite is most famous for its occurrence in Norway, particularly in the Larvik area, which is located along the southeastern coast of the country. This region has extensive deposits of larvikite, and it is often referred to as “Blue Pearl Granite” due to its striking blue-grey to silver-gray appearance with labradorite iridescence.
- Canada: Small occurrences of larvikite have been reported in Canada, primarily in the province of Quebec. These deposits are not as extensive as those in Norway but have similar mineralogical characteristics.
- Russia: Some deposits of larvikite can be found in Russia, particularly in the Kola Peninsula in the far northwest of the country. These Russian larvikite occurrences are less well-known than the Norwegian ones.
- Other Occasional Locations: Larvikite can also be found in limited quantities in other parts of the world, including the United States and Finland, but these occurrences are relatively rare and not as significant as those in Norway.
Overall, while larvikite is found in various parts of the world, it is most abundant and well-known in Norway, where it has a rich history of use in construction and decorative applications due to its unique appearance and durability.
Physical Characteristics of Larvikite

Larvikite is a distinctive igneous rock with several notable physical characteristics that make it stand out:
- Color: Larvikite is typically blue-grey to silver-gray in color. What sets it apart is the presence of labradorite feldspar, which can display iridescent blue or silver schiller, giving the rock a captivating and unique visual appeal.
- Texture: Larvikite often has a coarse-grained texture, meaning it contains relatively large mineral crystals. This texture is a result of the slow cooling of the magma from which it forms, allowing for the growth of larger feldspar crystals.
- Mineral Composition: The primary mineral in larvikite is oligoclase feldspar, which gives the rock its predominant color. It also contains other minerals such as hornblende, augite, and sometimes magnetite or ilmenite, contributing to its overall composition.
- Iridescence: The presence of labradorite feldspar in larvikite is responsible for its iridescent qualities. This labradorescence is an optical effect where the colors appear to change and shimmer when the rock is viewed from different angles or under varying lighting conditions.
- Hardness: Larvikite is relatively hard and durable, with a Mohs hardness rating of approximately 6 to 6.5. This hardness makes it suitable for various applications, including as a construction material and for decorative purposes.
- Density: Larvikite has a density that varies depending on its specific mineral composition and porosity but typically falls in the range of 2.63 to 2.70 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Polishability: Larvikite can be polished to a high sheen, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. Its natural luster, combined with its iridescence, makes it a popular choice for decorative surfaces such as countertops and tiles.
- Veining and Patterns: Depending on the specific quarry and location, larvikite may exhibit unique veining patterns or variations in color and schiller, adding to its aesthetic diversity.
These physical characteristics, especially its captivating appearance and durability, make larvikite a sought-after material for a wide range of architectural, interior design, and decorative applications. It is often used in the construction of countertops, flooring, wall cladding, and ornamental pieces due to its ability to add a touch of elegance and visual intrigue to various spaces.
Uses of Larvikite

Larvikite’s distinctive appearance and durability make it a versatile and sought-after material for a variety of architectural, decorative, and practical applications. Some of the common uses of larvikite include:
- Countertops: Larvikite is a popular choice for kitchen and bathroom countertops due to its durability, resistance to staining, and elegant appearance. Its polished surface enhances the overall aesthetic of these spaces.
- Flooring: Larvikite tiles are used for flooring in both residential and commercial settings. Its hard surface can withstand high foot traffic, and its unique coloration adds a touch of sophistication to interior spaces.
- Wall Cladding: Larvikite slabs or tiles are employed as wall cladding materials in homes, offices, and public buildings. The iridescent properties of larvikite create visually appealing accent walls.
- Monuments and Sculptures: Larvikite’s durability and attractive appearance make it suitable for creating monuments, sculptures, and other artistic installations. Its polished surface can highlight intricate details and designs.
- Interior Décor: Larvikite is used in interior decor items such as tabletops, fireplace surrounds, and ornamental pieces. Its striking visual effects add a touch of luxury to these items.
- Landscaping: In outdoor landscaping projects, larvikite may be used for paving walkways, creating outdoor seating areas, or as decorative elements in gardens and parks.
- Jewelry: Larvikite is sometimes used in the creation of jewelry items. Its iridescence and unique appearance can make for eye-catching gemstones or beads.
- Architectural Features: It can be employed in architectural elements such as columns, pillars, and accent pieces to enhance the aesthetics of buildings and structures.
- Cemetery Headstones: Due to its durability, larvikite is occasionally used for crafting cemetery headstones and grave markers.
- Dimension Stone: Larvikite is quarried and cut into various dimensions to meet specific construction and design requirements. These customized pieces can be used for diverse applications.
- Astronomical Equipment: Larvikite is known for its low thermal expansion properties, making it suitable for use in optical equipment such as telescope mirrors and lenses.
- Healing Crystals: Some believe that larvikite possesses metaphysical and healing properties. It is said to help with grounding, self-discovery, and protection.

Overall, larvikite’s ability to combine durability with a captivating appearance makes it a popular choice for enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of interior and exterior spaces, as well as for various artistic and decorative purposes. Its versatility and unique visual qualities make it a valued material in the worlds of architecture, design, and art.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!