How much do you know about the types of crystals?
For ordinary gemstones, the higher the clarity, the higher the value; in the world of crystal, in addition to clarity, whether the inclusions are beautiful and rare will also have a significant impact on the value of the crystal.
Can’t tell the difference between the various crystal varieties?
Divide by color
- White crystal
White crystal is also a colorless crystal, which is a colorless and transparent single crystal quartz, and it is also the most common crystal variety on the market.

The value of ordinary white crystal is not high, and it is better to have high purity. But when other inclusions are encased, their appearance and value change.

The value of ordinary white crystal is not high, and it is better to have high purity. But when other inclusions are encased, their appearance and value change.
- citrine
Citrine, common colors are light yellow, yellow, golden yellow, brown yellow, orange yellow.
The origin of the color may be related to the paired presence of iron in the crystal.
Natural citrine is produced less in nature, often associated with amethyst and crystal clusters, and most of the brightly colored citrine on the market is made of amethyst heating treatment or synthetic citrine.

- Pink crystal

Pink crystal
Pink crystal, also known as hibiscus stone, can be pinkish-white, light pink to pink, pinkish-purple. It is colored by the presence of trace amounts of Mn and Ti in the ingredients.
In some cases, hibiscus can contain tiny needle-like rutile inclusions arranged in parallel, allowing for starlight when polished into cabochons or spheres.
The color of pink crystal is also a bit unstable, it will fade when heated, and the color will fade after long-term exposure.
- amethyst
Amethyst, i.e., transparent to translucent purple crystal.
The color saturation of amethyst is deep and light, and high-quality amethyst is one of the most jeweled and popular varieties of crystal.
Amethyst contains trace amounts of iron, which is also the key to the cause of amethyst’s color.

However, it should be noted that the color center in amethyst will be destroyed and fade under heat or sun exposure.
Tea quartz, also known as smoky quartz, refers to transparent crystals with smoky, brown and brown colors.
When the color is relatively dark, dark brown to black, it is called ink crystal.

Most of the natural tea trizes are light brown, and dark brown smoky quartz is generally formed by irradiation of colorless or light brown crystals. Light brown tea crystal turns into white crystal when heated.
- Ametrine
Ametrine is a two-color crystal in which purple and yellow coexist on the same crystal. Purple and yellow each occupy a portion of the crystal, and there is a clear boundary between the two colors.
Some studies believe that the bicolor of natural ametrine is caused by the double crystal. The popular cheap bowl of ametrine in the market is mostly the product of heat treatment when the amethyst is half covered.

- Green crystal
Pale green, yellow-green crystals, often called green crystals, are related to bivalent iron.
Natural green crystal is scarce in nature, and there is almost no naturally produced green crystal on the market, and most of the green crystal is an intermediate product of amethyst in the process of heating into citrine.

Divided by inclusions
- Ghost Crystal
Ghost crystal is a crystal that encapsulates some mudstone and other minerals during the growth of white crystal, and after grinding and molding, those that form some special scenery in the ghost crystal are called vision crystals and phantom crystals.
In the process of rapid crystal growth, the rejection of foreign impurities on the crystal plane will gradually weaken, making it easier for foreign impurities to grow on the mirror surface and form inclusions.
Phantom crystals are formed when crystal inclusions grown into a supersaturated solution form large crystals that are similar in shape to the original small crystals. Phantom crystals are the result of the combination of material and non-material inclusions (growth lines).
Ghost crystals are of different colors and varieties depending on the color of the inclusions, and the most valuable is the “Green Ghost” crystal containing chlorite.

When the color of the volcanic mud changes, there are also white ghosts, red ghosts, pink ghosts, yellow ghosts, purple ghosts and other color varieties.
In addition to the green ghost, the “Four Seasons Ghost”, which contains white, yellow, green, and red ghosts in the same crystal, is also more valuable.
Contains inclusions such as needle-like, fibrous rutile, tourmaline and actinolite to form crystallization.
In colorless and transparent crystals, there are needle-like, hair-like or fibrous mineral inclusions, which are called hair crystals because the shape of these inclusions resembles human hair.

The “hair strands” in the hair crystal are divided into gold, red, green, black and silver and other colors, and there are varieties on the market according to the color of the hair crystal: blonde hair crystal, red copper hair, black hair crystal, green hair crystal and so on.

The classification of hair crystals according to color is relatively simple, clear, and easy to understand; But this kind of name tends to be more market habits. The relatively professional classification method should be divided according to the mineral composition of the hair strands it contains
.
Rutile hair crystals:

The hair strands are rutile, often distributed in bundles and radial filaments, with golden yellow, light yellow, brownish yellow, etc.
Actinolite hair crystals: Hair strands are green-dark green (when viewed under a 10x large mirror, the hair strands are flattened and long, thus distinguishing it from tourmaline hair crystals).

Tourmaline crystals: common black, green; The composition of the hair strands is tourmaline (characteristics: magnified observation, the cross-section of the hair strands is curved triangle), which is more common in the market.

Limonite crystals: Hair strands are red and maroon-red.

Blue Hair Crystal: The hair is a natural blue liner inclusion, giving it a dreamy blue color. However, most of the blue threads will not be particularly long, and there are also dyed blue hair crystals on the market, so pay attention to distinguish.

- Titanium crystal
When the needle-like minerals in the hair crystal are densely packed into plates, it is called “titanium crystal”, and the value of titanium crystal is higher than that of hair crystal.

When the needle-like minerals in the hair crystal are densely packed into plates, it is called “titanium crystal”, and the value of titanium crystal is higher than that of hair crystal.
- Rabbit
When the needle-like, hair-like or fibrous mineral inclusions in the crystal are very delicate and dense, and the shape is like fine hair that is softly entangled, it is more like the soft hair of animals, and is figuratively called “rabbit hair crystal“.
When the needle-like, hair-like or fibrous mineral inclusions in the crystal are very delicate and dense, and the shape is like fine hair that is softly entangled, it is more like the soft hair of animals, and is figuratively called “rabbit hair crystal”.

According to the different mineral components contained, rabbit hair crystals have white rabbit hair, green rabbit hair, red rabbit hair, yellow rabbit hair, gray rabbit hair and other colors.

- Glue flowers
In the process of crystal formation, the volcanic magma in the environment flows into the cracks where the crystal develops, and the glue flower crystal is formed.

The common colors of glue crystals are brown, maroon, brownish, yellow, and yellow. The varieties are generally divided into yellow gum flowers and red gum flowers.
Because the color distribution of the watering crystal is different, it often presents some wonderful patterns and scenes.

When the white crystal contains dense scale-like, fine-needle-like, and sometimes “beetle-leg-shaped” iron oxide mineral inclusions such as hematite and wyolite, showing elegant pink, brown, and bright red, it is strawberry crystal.

- Rainbow Crystal
Some crystals with cracks can also show bright halos, forming rainbow crystals
Due to the presence of fine bubbles inside, or liquid filled in the cracks of the crystal, when light shines on the bubbles, the liquid in the cracks. Interference occurs to create a rainbow.
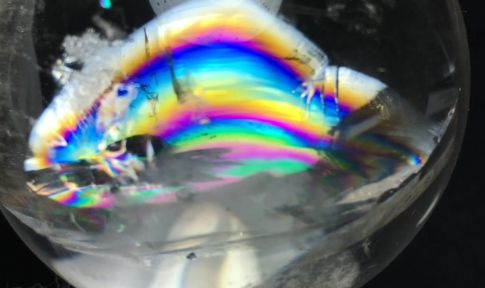
Due to the presence of fine bubbles inside, or liquid filled in the cracks of the crystal, when light shines on the bubbles, the liquid in the cracks. Interference occurs to create a rainbow.
- Water gall crystal, oil gall crystal
Crystals that contain liquid inclusions inside transparent crystals are called “water gall crystals or oil crystals”.
The formation of water gall crystals results from the capture of diagenetic metallogenic solutions during crystal growth, commonly found in magmatic hydrothermal deposits.
According to the state of the water bitulite, the water bitus crystal can be divided into liquid phase water bilicle crystal (pure liquid inside), gas-liquid biphasic water bitus crystal (there is gas and liquid in the water bilite), and liquid-solid biphasic water bile (liquid and solid inclusions in the water bilibul) crystal.
According to the state of the water bitulite, the water bitus crystal can be divided into liquid phase water bilicle crystal (pure liquid inside), gas-liquid biphasic water bitus crystal (there is gas and liquid in the water bilite), and liquid-solid biphasic water bile (liquid and solid inclusions in the water bilibul) crystal.

For the liquid inclusions inside the crystal in the form of yellow oil droplets, and the solid inclusions present small black pieces, we call them oil gall crystals. The more well-known production place of oil gall crystal is Pakistan, but in fact, the origin of oil gall crystal is far from limited to this, but merchants generally love to introduce the origin of Pakistan.
In terms of value, the value of oil gall crystal is higher than that of water gall crystal.

In terms of value, the value of oil gall crystal is higher than that of water gall crystal.
- Crystal within crystal
When a piece of crystal penetrates or completely encloses another crystal, this peculiar phenomenon is called “crystal-within-crystal”.

Solid inclusions in crystals can also contain garnet, fluorite, pyrite, solid asphalt, etc.
Due to the different inclusions, the scene inside the crystal is also different, and some relatively rare crystal-in-crystal crystals also have a certain collection value in the market.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!