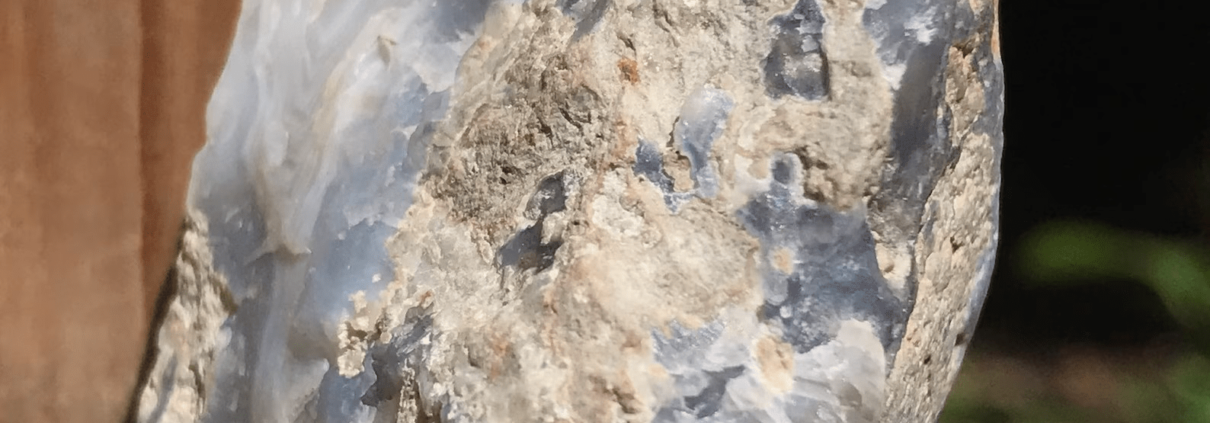
Ellensburg Blue Agate
Ellensburg Blue Agate is a rare and prized variety of agate found primarily in the Kittitas Valley near Ellensburg, Washington, USA. It’s renowned for its striking blue hues, ranging from sky blue to deep azure, often accented with white, grey, or brown patterns. This gemstone’s mesmerizing colors and unique patterns make it highly sought after by collectors and jewelry enthusiasts worldwide.
 Ellensburg Blue Agate: Uncover the Secrets of Washington’s Rare Gemstone – Rock Seeker
Ellensburg Blue Agate: Uncover the Secrets of Washington’s Rare Gemstone – Rock Seeker
Geologically, Ellensburg Blue Agate formed millions of years ago during the Miocene epoch when volcanic activity and silica-rich fluids permeated through cavities in ancient basalt flows. Over time, these fluids deposited layers of microscopic quartz crystals, creating the banded and translucent appearance characteristic of agate. What sets Ellensburg Blue apart is its distinctive blue coloration, believed to result from the presence of copper and other trace elements within the silica solution during formation.
The discovery of Ellensburg Blue Agate traces back to the early 20th century when farmers and miners in the Kittitas Valley stumbled upon these unique gemstones while plowing fields or mining for other minerals. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s and 1970s that Ellensburg Blue gained significant attention among lapidary enthusiasts and collectors. The gemstone’s popularity surged as its rarity became apparent due to limited accessibility to the specific geological formations where it occurs.
Since its discovery, Ellensburg Blue Agate has become a treasured symbol of Washington state’s geological heritage. Its scarcity and captivating beauty have made it a prized addition to gemstone collections and a favored choice for jewelry designers seeking unique and ethereal gemstones.
Despite its popularity, Ellensburg Blue Agate remains relatively rare, and mining efforts have been restricted due to environmental concerns and land ownership issues. Consequently, specimens of this exquisite gemstone are highly valued and cherished by those fortunate enough to possess them, adding to its allure and mystique in the world of gemstones.
Contents
- Geological Formation
- Physical Properties and Unique characteristics of Ellensburg Blue Agate
- Locations where Ellensburg Blue Agate is found
- Popular Uses and Applications
- Chemical composition and structure Comparison with other types of agate
Geological Formation

Ellensburg Blue Agate formed through a combination of geological processes over millions of years. Its creation is intimately tied to the volcanic activity that shaped the landscape of the Pacific Northwest region of the United States.
The story begins during the Miocene epoch, approximately 5 to 23 million years ago, when the area around Ellensburg, Washington, experienced intense volcanic activity. During this time, massive basalt flows, rich in silica and other minerals, erupted from fissures in the Earth’s crust. As these molten lava flows cooled and solidified, they created vast layers of basalt rock that now form much of the underlying geology of the region.
Within these layers of basalt, cavities and fractures known as vesicles formed as gases escaped from the cooling lava. Over time, these voids became filled with silica-rich fluids, typically containing dissolved quartz and other minerals. These fluids percolated through the rock, depositing microscopic quartz crystals along the walls of the cavities.
The distinctive blue coloration of Ellensburg Blue Agate is believed to result from the presence of trace elements such as copper within the silica solution during the crystallization process. These trace elements can interact with the quartz crystals, imparting various shades of blue to the agate.
As the geological processes continued, pressure and temperature fluctuations, along with the movement of groundwater, contributed to the growth and alteration of the agate deposits. Over millions of years, layers of silica crystallized within the cavities, forming the characteristic banded and translucent patterns seen in agate specimens.
The eventual exposure of these agate-filled vesicles at the Earth’s surface, through erosion and uplift, allowed for their discovery by humans. Farmers, miners, and rockhounds in the Kittitas Valley began finding these striking blue gemstones in the 20th century, leading to the recognition and appreciation of Ellensburg Blue Agate as a unique and prized variety of agate.
Physical Properties and Unique characteristics of Ellensburg Blue Agate

Ellensburg Blue Agate possesses several unique physical properties that distinguish it from other varieties of agate and contribute to its desirability among collectors and jewelry enthusiasts:
- Color: The most distinctive feature of Ellensburg Blue Agate is its captivating blue coloration, ranging from delicate sky blue to intense azure. This unique hue is often accompanied by variations in tone and saturation, creating mesmerizing patterns within the gemstone.
- Translucency: Ellensburg Blue Agate exhibits varying degrees of translucency, allowing light to pass through the stone and accentuating its color and internal patterns. This property adds depth and luminosity to the gemstone, enhancing its visual appeal.
- Banding: Like other agates, Ellensburg Blue often displays banded patterns composed of alternating layers of different minerals or concentrations of impurities. These bands can vary in thickness and color, contributing to the gemstone’s overall aesthetic.
- Hardness: Agate, including Ellensburg Blue, typically has a hardness of 6.5 to 7 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively durable and suitable for use in jewelry. This hardness ensures that Ellensburg Blue Agate can withstand everyday wear without easily scratching or chipping.
- Chatoyancy: Some specimens of Ellensburg Blue Agate exhibit chatoyancy, also known as the “cat’s-eye” effect, where a band of light appears to move across the surface of the stone when viewed from different angles. This optical phenomenon adds dynamic visual interest to the gemstone.
- Inclusions: Ellensburg Blue Agate may contain various inclusions, such as small crystals, mineral deposits, or fractures, which can enhance its character and uniqueness. These natural features contribute to the individuality of each gemstone and may influence its value among collectors.
- Origin: The association with the Kittitas Valley near Ellensburg, Washington, lends a sense of provenance and rarity to Ellensburg Blue Agate. Its limited geographic occurrence and historical significance further enhance its allure and collectibility.
Overall, the combination of its striking blue color, translucency, unique patterns, and geological origin make Ellensburg Blue Agate a highly prized and sought-after gemstone among collectors and jewelry artisans.
Locations where Ellensburg Blue Agate is found

Ellensburg Blue Agate is primarily found in the Kittitas Valley near Ellensburg, Washington, USA. This region, located in central Washington state, is known for its unique geological formations and volcanic activity, which contributed to the formation of the agate deposits.
Within the Kittitas Valley, specific locations where Ellensburg Blue Agate has been discovered include:
- Teanaway River Area: The Teanaway River, a tributary of the Yakima River, flows through the eastern part of the Kittitas Valley. Agate hunters have reported finding Ellensburg Blue specimens along the riverbanks and within the surrounding hillsides.
- Manastash Ridge: Manastash Ridge, situated to the northwest of Ellensburg, is a popular destination for rockhounding enthusiasts seeking various gemstones and minerals, including Ellensburg Blue Agate. Agate deposits can be found in pockets and outcroppings throughout the ridge.
- Thorp Area: The community of Thorp, located northeast of Ellensburg, is another area where Ellensburg Blue Agate has been discovered. Rockhounds often explore the hillsides and creek beds in this vicinity in search of gemstone specimens.
- Canyon Road Area: Canyon Road, which winds through the Kittitas Valley, provides access to several promising agate hunting sites. Agate enthusiasts have reported finding Ellensburg Blue specimens in this area, particularly in gravel beds and exposed rock formations.
- Private Claims and Mines: Some portions of the Kittitas Valley where Ellensburg Blue Agate occurs are on private property or mining claims. Access to these areas may be restricted, but collectors with permission from landowners or claim holders may have the opportunity to search for specimens.
It’s important to note that Ellensburg Blue Agate is relatively rare, and not all locations within the Kittitas Valley yield significant quantities of this gemstone. Additionally, environmental regulations and land ownership considerations may impact access to certain areas. As such, rockhounding enthusiasts are encouraged to research local regulations and obtain any necessary permits before exploring potential collecting sites.
Popular Uses and Applications
 Ellensburg Blue Agate – Central Washington
Ellensburg Blue Agate – Central Washington
Ellensburg Blue Agate’s captivating beauty and unique properties make it a sought-after gemstone for various uses and applications:
- Jewelry: One of the most popular uses for Ellensburg Blue Agate is in jewelry design. Gem cutters and jewelry artisans often fashion it into cabochons, beads, pendants, and other ornamental pieces. Its striking blue color, translucency, and distinctive patterns make it an eye-catching choice for rings, earrings, necklaces, and bracelets.
- Collector Specimens: Given its rarity and geological significance, Ellensburg Blue Agate is highly prized by gemstone collectors. Collectors seek out high-quality specimens with vibrant coloration, unique patterns, and desirable inclusions for display in private collections or museums.
- Lapidary Art: Ellensburg Blue Agate is valued by lapidaries and stone carvers for its workability and aesthetic appeal. Artists may incorporate it into sculptures, decorative objects, and intricate carvings, showcasing its natural beauty and enhancing interior or exterior spaces.
- Healing and Metaphysical Practices: In holistic healing and metaphysical practices, Ellensburg Blue Agate is believed to possess spiritual properties that promote calmness, harmony, and emotional balance. Some individuals use it as a meditation aid, a talisman for protection, or a tool for enhancing intuition and self-expression.
- Ornamental Decor: Polished slices or chunks of Ellensburg Blue Agate are often used as decorative accents in home decor and interior design. These natural gemstone pieces can be displayed on shelves, tabletops, or mantels, adding a touch of elegance and natural beauty to living spaces.
- Gifts and Souvenirs: Ellensburg Blue Agate jewelry, specimens, and decorative items are popular choices for gifts and souvenirs. Visitors to the Kittitas Valley and surrounding areas often seek out Ellensburg Blue products as mementos of their travels or as unique gifts for loved ones.
- Educational Purposes: Ellensburg Blue Agate’s geological origin and distinctive features make it a valuable educational resource for geology enthusiasts, students, and researchers. Studying the formation and properties of Ellensburg Blue provides insights into volcanic processes, mineralogy, and the natural history of the Pacific Northwest region.
Overall, Ellensburg Blue Agate’s versatility, beauty, and cultural significance contribute to its enduring popularity and wide range of applications in art, jewelry, decor, and holistic practices.
Chemical composition and structure Comparison with other types of agate

Ellensburg Blue Agate, like other varieties of agate, is primarily composed of microcrystalline quartz, also known as chalcedony. However, what sets it apart is its unique chemical composition and structure, particularly regarding its distinctive blue coloration.
- Chemical Composition:
- Quartz (SiO2): As the main component, quartz accounts for the majority of Ellensburg Blue Agate’s composition. It forms the microscopic crystals that give the agate its hardness and translucency.
- Trace Elements: Ellensburg Blue Agate’s blue coloration is believed to be the result of trace elements present during its formation, particularly copper. Other elements, such as iron, manganese, and titanium, may also contribute to the gemstone’s color and appearance.
- Structure:
- Banded Structure: Like other agates, Ellensburg Blue often exhibits a banded structure, consisting of alternating layers of different minerals or concentrations of impurities. These bands may vary in thickness and color, creating unique patterns within the gemstone.
- Microcrystalline Texture: Agate is characterized by its fine-grained, microcrystalline texture, with individual quartz crystals too small to be seen with the naked eye. This texture contributes to the gemstone’s smooth and polished appearance.
- Comparison with Other Agates:
- Color Variation: While agates come in a wide range of colors, including white, grey, brown, and various shades of blue, Ellensburg Blue Agate is distinguished by its intense and vibrant blue hues, which are less commonly found in other agate varieties.
- Origin and Rarity: Ellensburg Blue Agate’s specific geological origin in the Kittitas Valley near Ellensburg, Washington, contributes to its rarity and uniqueness compared to other agate types. Its limited geographic occurrence and historical significance enhance its value among collectors.
- Optical Phenomena: Some specimens of Ellensburg Blue Agate may exhibit optical phenomena such as chatoyancy (cat’s-eye effect) or iridescence, adding to their visual appeal and distinguishing them from other agates with different optical properties.
In summary, while Ellensburg Blue Agate shares many characteristics with other types of agate, including its chemical composition, banded structure, and microcrystalline texture, its distinctive blue coloration, trace element content, and geological origin make it a prized and sought-after gemstone with unique properties and aesthetic appeal.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!