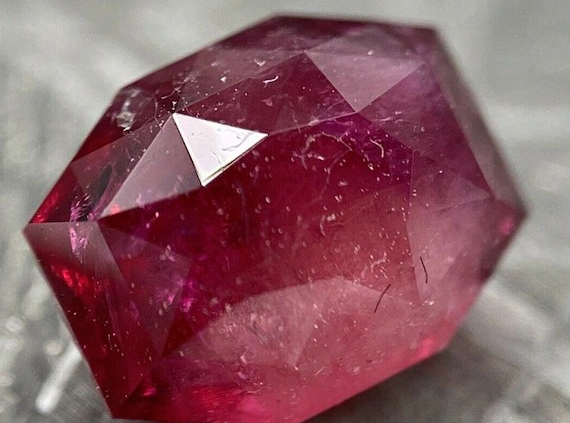
Bixbite / Red Beryl
Bixbite is a trade name used to refer to red beryl, a rare gemstone that is found in only a few locations worldwide. Red beryl was first discovered in 1904 in the Wah Wah Mountains of Utah, USA. The gemstone is highly sought after by collectors and jewelry enthusiasts due to its vivid red color and scarcity.
Red beryl gets its color from traces of manganese and other minerals present in the crystal structure. The gemstone is typically small in size, with most specimens measuring less than one carat. Larger red beryl stones are extremely rare and can command high prices in the gemstone market.
Because of its rarity, red beryl is considered one of the most valuable gemstones in the world. It is often compared to other rare gems like diamond, emerald, and sapphire in terms of its desirability and value.

Contents
- Characteristics of red beryl
- Brief history of the discovery of red beryl
- Formation of red beryl
- Physical Properties
- Chemical composition and crystal structure of red beryl
- Optical properties
- Geological Occurrence
- Mining and Extraction
- Uses and Applications
- Locations where red beryl can be found
- Summary of key points
- FAQ
- References
Characteristics of red beryl
Red beryl is a rare and valuable gemstone that is known for its striking red color and unique crystal structure. Here are some of its characteristics:
- Color: Red beryl is known for its vivid red color, which can range from a deep red to a pinkish-red hue. The gemstone gets its color from traces of manganese that are present in its crystal structure.
- Hardness: Red beryl has a hardness of 7.5-8 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively hard and durable. This means that it is less prone to scratching and damage than some other gemstones.
- Crystal Structure: Red beryl has a hexagonal crystal structure and belongs to the hexagonal system of minerals. It has a unique set of crystallographic axes that give it its distinctive shape.
- Transparency: Red beryl is typically transparent, although some specimens may have inclusions or other imperfections that can affect their clarity.
- Rarity: Red beryl is one of the rarest gemstones in the world, with only a few known locations where it can be found. The gemstone is primarily found in the Wah Wah Mountains of Utah, USA, although smaller deposits have been discovered in other parts of the world, including Mexico and Afghanistan.
- Value: Red beryl is highly valued by collectors and jewelry enthusiasts due to its rarity, unique color, and high demand. It is often compared to other rare gemstones like diamond, emerald, and sapphire in terms of its desirability and value.
Overall, red beryl is a beautiful and rare gemstone that is prized for its unique properties and striking appearance.

Brief history of the discovery of red beryl
The discovery of red beryl is a relatively recent event in the history of mineralogy and gemology. Here is a brief history of the discovery of red beryl:
In 1904, Maynard Bixby, a mineralogist and prospector, discovered a new type of gemstone in the Thomas Range of western Utah. The gemstone was initially thought to be red emerald, but later analysis revealed that it was a distinct mineral species, which was named bixbite in honor of Maynard Bixby.
For many years, bixbite was known only as a curiosity to mineral collectors and was not widely recognized as a gemstone. It was not until the 1950s that commercial mining of bixbite began in Utah, and the gemstone was given the name “red beryl” to distinguish it from other types of beryl minerals.
Today, red beryl is still one of the rarest and most sought-after gemstones in the world. It is primarily found in the Wah Wah Mountains of Utah, USA, although smaller deposits have been discovered in other parts of the world, including Mexico and Afghanistan. The history of the discovery of red beryl is a testament to the ongoing search for new mineral species and the enduring fascination with rare and beautiful gemstones.

Formation of red beryl
The formation of red beryl is a complex process that involves a combination of geological factors and specific environmental conditions. Here is an overview of the formation of red beryl:
Red beryl is formed in hydrothermal veins that are associated with rhyolite volcanic rocks. These veins are believed to have formed as a result of hot, mineral-rich fluids that were forced up from the Earth’s mantle and circulated through fractures in the surrounding rock.
The fluids that gave rise to red beryl are thought to have originated from a source of magma deep within the Earth’s crust. As the magma cooled and crystallized, it released water and other volatile compounds that were incorporated into the surrounding rocks and created the conditions necessary for the formation of red beryl.
The specific chemical and physical conditions required for the formation of red beryl are still not fully understood, but it is thought that the presence of certain trace elements, including manganese, iron, and cesium, may play a key role in the gemstone’s formation.
The process of red beryl formation likely involved a combination of high temperatures, high pressures, and the presence of mineral-rich fluids that were saturated with dissolved beryllium, aluminum, and other elements. Over time, these fluids crystallized into the distinctive hexagonal crystal structure that is characteristic of red beryl.
The rarity and value of red beryl are due in part to the unique combination of geological factors and specific environmental conditions that are required for its formation. As a result, red beryl is considered one of the most precious gemstones in the world.
Physical Properties
- Chemical Composition: Red beryl is a beryllium aluminum silicate mineral with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6.
- Hardness: Red beryl has a hardness of 7.5-8 on the Mohs scale, which makes it relatively hard and durable. However, it is still less hard than some other gemstones such as diamond, sapphire, and ruby.
- Density: The density of red beryl ranges from 2.66 to 2.70 g/cm3, which is slightly higher than the density of most other beryl varieties.
- Refractive Index: Red beryl has a refractive index of 1.566-1.574, which is relatively high and gives it excellent brilliance and sparkle.
- Dispersion: The dispersion of red beryl is 0.014, which is lower than some other gemstones but still contributes to its fire and brilliance.
- Lustre: Red beryl has a vitreous to sub-adamantine lustre, which means that it has a shiny, glassy appearance.
- Cleavage: Red beryl has no distinct cleavage, which means that it does not split along specific planes or directions.
- Color: As the name suggests, red beryl is known for its vibrant red color, which is caused by the presence of manganese in its crystal structure. The color can range from a deep red to a pinkish-red hue.
Overall, the physical properties of red beryl make it a unique and highly sought-after gemstone with excellent durability, brilliance, and color.
Chemical composition and crystal structure of red beryl
Red beryl has a chemical composition of Be3Al2(SiO3)6, which is a beryllium aluminum silicate mineral. It belongs to the beryl group of minerals, which includes other gemstones such as emerald, aquamarine, and morganite.
The crystal structure of red beryl is hexagonal, meaning that its crystal lattice is composed of repeating units in a six-sided shape. This crystal structure is characteristic of all beryl minerals, which are classified as cyclosilicates.
In the crystal structure of red beryl, beryllium and aluminum ions are arranged in octahedral coordination, while silicon ions occupy tetrahedral sites in between the octahedra. The presence of manganese within the crystal structure gives red beryl its distinctive red color, which can range from a deep red to a pinkish-red hue.
The specific arrangement of atoms within the crystal structure of red beryl gives rise to its unique physical and optical properties, including its high refractive index, excellent brilliance and sparkle, and durability. The chemical composition and crystal structure of red beryl are what make it a rare and valuable gemstone.
Optical properties
Red beryl has excellent optical properties, which contribute to its unique beauty and high value as a gemstone. Here are some of its optical properties:
- Refractive index: Red beryl has a relatively high refractive index, ranging from 1.566 to 1.574. This means that light is bent or refracted more as it passes through the gemstone, resulting in excellent brilliance and sparkle.
- Dispersion: Red beryl has a relatively low dispersion of 0.014. Dispersion refers to the ability of a gemstone to split white light into its component colors, creating a rainbow effect. While red beryl has lower dispersion than some other gemstones, such as diamond or sapphire, it still exhibits a noticeable amount of fire and brilliance.
- Birefringence: Red beryl has a low birefringence of 0.008. Birefringence is the difference in refractive index between two perpendicular planes in a gemstone. Red beryl’s low birefringence means that it does not produce double images or appear blurry under magnification.
- Pleochroism: Red beryl exhibits weak pleochroism, meaning that it shows slightly different colors when viewed from different angles. In the case of red beryl, it can appear slightly pinkish-red or orangish-red when viewed from different directions.
- Lustre: Red beryl has a vitreous to sub-adamantine lustre, which gives it a shiny, glassy appearance.
Overall, red beryl’s excellent optical properties make it a highly desirable gemstone, prized for its vibrant red color, brilliance, and rarity.
Geological Occurrence
Red beryl is a rare and valuable gemstone that is found in only a few locations worldwide. It is primarily found in association with rhyolite volcanic rocks, which are high-silica, low-iron volcanic rocks that are commonly associated with caldera complexes.
The main geological occurrence of red beryl is in the Wah Wah Mountains of Beaver County, Utah, USA, where it is found in a rhyolite host rock. The red beryl-bearing rhyolite at this location is believed to be part of a volcanic ash-flow tuff that erupted about 18 million years ago. The rhyolite is highly fractured and altered, and the red beryl occurs in miarolitic cavities (small, irregular cavities in the rock that are filled with mineral crystals) within the rhyolite.
Other notable occurrences of red beryl include the Black Range district of New Mexico, USA, and the Thomas Range in Juab County, Utah, USA. However, the red beryl deposits at these locations are much smaller and less significant than those in the Wah Wah Mountains of Utah.
The formation of red beryl is believed to be associated with hydrothermal activity, where hot, mineral-rich fluids circulated through fractures in the rhyolite host rock and deposited beryl and other minerals in miarolitic cavities. The presence of manganese within the crystal structure of red beryl is believed to be the result of the interaction of the mineralizing fluids with manganese-rich sediments and rocks in the surrounding area.
Overall, the geological occurrence of red beryl is relatively rare, and the gemstone is considered to be one of the rarest and most valuable gemstones in the world.
Mining and Extraction
Mining and extraction of red beryl is a challenging process due to the rarity and small size of the deposits. In addition, the mineral occurs in miarolitic cavities that are often small and irregularly shaped, making extraction difficult.
The primary commercial source of red beryl is the Ruby-Violet Claims in the Wah Wah Mountains of Beaver County, Utah, USA. The mining of red beryl in this location is done through small-scale, underground mining operations, which involve drilling and blasting of the rhyolite host rock to access the miarolitic cavities containing the red beryl crystals.
Once the red beryl-bearing rhyolite has been mined, it is crushed and sorted to separate the red beryl crystals from the waste rock. The sorting process is typically done by hand, as the red beryl crystals are small and can be easily damaged by mechanical sorting methods.
After the red beryl crystals have been separated from the waste rock, they are cleaned and graded according to their size, color, clarity, and overall quality. Red beryl is a highly valued gemstone, and high-quality specimens can fetch prices of several thousand dollars per carat.
Overall, the mining and extraction of red beryl is a labor-intensive and costly process due to the rarity and small size of the deposits. However, the gemstone’s unique beauty and high value make it a sought-after collectible for gemstone enthusiasts and collectors.
Uses and Applications
Red beryl is a rare and highly valued gemstone that is primarily used in jewelry. Due to its vibrant red color and excellent optical properties, red beryl is a popular choice for collectors and jewelry enthusiasts who appreciate its rarity and beauty.
Red beryl is typically cut into faceted gemstones for use in rings, earrings, necklaces, and other jewelry items. The gemstone is prized for its intense red color, which is caused by trace amounts of manganese within the crystal structure. Red beryl is often used as a center stone in engagement rings and other high-end jewelry pieces, where its rarity and value make it a unique and cherished choice.
In addition to its use in jewelry, red beryl has also been used in scientific research due to its unique crystal structure and properties. For example, red beryl has been studied for its potential use in laser technology, as its crystal structure allows for the emission of a narrow beam of coherent light.
Overall, the primary use of red beryl is in the production of high-end jewelry items. The gemstone’s rarity, unique color, and excellent optical properties make it a highly prized and valuable addition to any gemstone collection or jewelry collection.

Locations where red beryl can be found
Red beryl is an extremely rare gemstone and is found in only a few locations worldwide. The most significant source of red beryl is the Wah Wah Mountains of Beaver County, Utah, USA, where the gemstone was first discovered. Other notable locations where red beryl has been found include:
- The Black Range district of New Mexico, USA: This location is known for producing high-quality red beryl crystals, although the deposits are small and sporadic.
- The Thomas Range in Juab County, Utah, USA: This location is known for producing larger red beryl crystals, although the deposits are also relatively small.
- The Sierra de la Lagunita in San Luis Potosi, Mexico: This location is the only known occurrence of red beryl outside of the United States. The deposits are small and sporadic, and the gemstone is typically found in association with volcanic rocks.
Overall, red beryl is an extremely rare gemstone, and the locations where it can be found are limited. The gemstone’s rarity and unique beauty make it a highly prized addition to any gemstone collection.
Summary of key points
- Red beryl is a rare and highly valued gemstone that is primarily used in jewelry.
- The gemstone’s vibrant red color is caused by trace amounts of manganese within the crystal structure.
- Red beryl is typically found in miarolitic cavities within rhyolite host rock.
- The primary commercial source of red beryl is the Ruby-Violet Claims in the Wah Wah Mountains of Beaver County, Utah, USA.
- Other notable locations where red beryl has been found include the Black Range district of New Mexico, USA, the Thomas Range in Juab County, Utah, USA, and the Sierra de la Lagunita in San Luis Potosi, Mexico.
- Mining and extraction of red beryl is a labor-intensive and costly process due to the rarity and small size of the deposits.
- Red beryl is primarily used in jewelry, where it is cut into faceted gemstones for use in rings, earrings, necklaces, and other jewelry items.
- The gemstone’s rarity, unique color, and excellent optical properties make it a highly prized and valuable addition to any gemstone collection or jewelry collection.
FAQ
What is red beryl?
Red beryl is a rare and highly valued gemstone that is primarily used in jewelry. The gemstone’s vibrant red color is caused by trace amounts of manganese within the crystal structure.
Where is red beryl found?
Red beryl is found in only a few locations worldwide, with the primary commercial source being the Ruby-Violet Claims in the Wah Wah Mountains of Beaver County, Utah, USA.
How is red beryl mined and extracted?
Mining and extraction of red beryl is a labor-intensive and costly process due to the rarity and small size of the deposits. The gemstone is typically found in miarolitic cavities within rhyolite host rock and is extracted through a combination of hand tools, drilling, and blasting.
What is the value of red beryl?
Red beryl is one of the rarest gemstones in the world, and as such, it is extremely valuable. The value of red beryl is determined by a variety of factors, including its size, color, clarity, and cut.
What are the uses of red beryl?
Red beryl is primarily used in jewelry, where it is cut into faceted gemstones for use in rings, earrings, necklaces, and other jewelry items. The gemstone’s rarity, unique color, and excellent optical properties make it a highly prized and valuable addition to any gemstone collection or jewelry collection.
How is red beryl different from other gemstones?
Red beryl is different from other gemstones in several ways. First, it is extremely rare, with only a few known deposits worldwide. Second, it has a unique crystal structure and optical properties that allow for the emission of a narrow beam of coherent light, making it potentially useful in laser technology. Finally, its vibrant red color is caused by trace amounts of manganese within the crystal structure, making it unlike any other gemstone.
Can red beryl be treated or enhanced?
Red beryl is not typically treated or enhanced in any way, as the gemstone is already highly prized for its natural color and clarity.
What is the difference between red beryl and other red gemstones?
Red beryl is often compared to other red gemstones, such as ruby and red spinel. While all of these gemstones share a similar color, they are chemically and structurally distinct. Red beryl is a beryllium aluminum silicate, while ruby is a variety of corundum and red spinel is a magnesium aluminum oxide.
What are some famous pieces of jewelry featuring red beryl?
Red beryl is a rare gemstone and is not commonly found in jewelry. However, some famous pieces of jewelry featuring red beryl include a ring worn by Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis and a necklace worn by actress Mila Kunis at the 2011 Oscars.
Is red beryl a birthstone?
Red beryl is not a traditional birthstone, but it is sometimes used as an alternative to traditional birthstones, such as ruby or garnet, for those born in the month of January.
References
- Groat, L. A., Giuliani, G., & Marshall, D. D. (2008). Red beryl. Gems & Gemology, 44(2), 118-135.
- Hurlbut, C. S., & Kammerling, R. C. (1991). Gemology. John Wiley & Sons.
- Koivula, J. I., Kammerling, R. C., Fritsch, E., & Rossman, G. R. (1994). Red beryl: a new find in Utah. Gems & Gemology, 30(4), 228-241.
- Laurs, B. M., & Koivula, J. I. (2002). A study of the Utah deposit of red beryl. Gems & Gemology, 38(1), 2-24.
- Schmetzer, K., & Hänni, H. A. (1988). Red beryl from Juab County, Utah, USA. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie-Monatshefte, 511-524.
- Sinkankas, J. (1981). Gemstones of North America. Geoscience Press.
- Webster, R. (2006). Gems: Their sources, descriptions and identification. Butterworth-Heinemann.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!