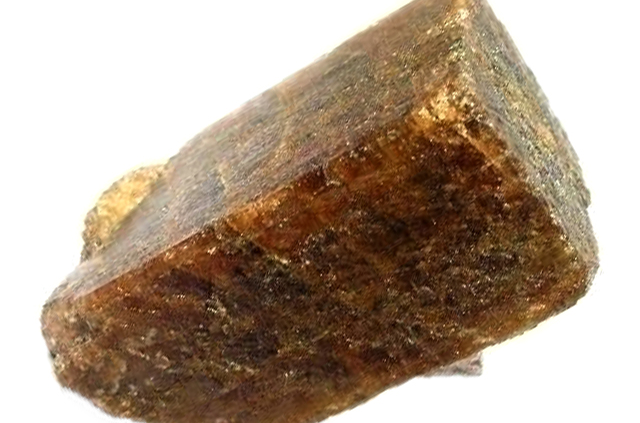
Andalusite
Andalusite is a mineral that holds significant importance due to its unique crystal structure, distinctive physical properties, and its utilization in various industrial applications. It belongs to the aluminosilicate mineral group and is characterized by its remarkable thermal stability, making it an essential component in refractory materials used in high-temperature environments. Its name is derived from the region of Andalusia in Spain, where the mineral was first discovered.
 Andalusite Mineral
Andalusite Mineral
 Andalusite Mineral
Andalusite Mineral
 Andalusite_(Chiastolite)
Andalusite_(Chiastolite)
Definition: Andalusite is a naturally occurring aluminum silicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system, forming prismatic crystals that often display a distinctive cross-shaped pattern when viewed in cross-section. This property, known as pleochroism, is a key identifying feature of andalusite. The mineral can exhibit various colors, including green, brown, and reddish-brown, and its hardness ranges from 6.5 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively hard and durable.
Overview: Andalusite is primarily found in metamorphic rocks that have undergone high levels of heat and pressure during their formation. It is a mineral that is often associated with medium- to high-grade metamorphic terrains, indicating the intense geological conditions under which it is formed. The mineral’s formation is closely linked to regional metamorphism, contact metamorphism, and regional tectonic processes that lead to the crystallization of aluminosilicate minerals.
One of the most notable features of andalusite is its exceptional thermal stability. It exhibits a phenomenon called the “andalusite chiastolite cross” or “cross-fiber” pattern, which is a result of carbonaceous impurities creating different thermal expansion rates along different crystallographic directions. This unique property makes andalusite an invaluable material in refractory applications, where it can withstand high temperatures without significant deformation or breakdown.
Andalusite finds extensive use in industries such as refractories, ceramics, and porcelain production due to its ability to maintain its integrity under extreme temperature conditions. Its role in these applications involves providing structural stability, thermal insulation, and resistance to chemical and mechanical stresses.
In conclusion, andalusite is a mineral of considerable significance due to its distinct properties and its crucial role in various industrial sectors. Its remarkable thermal stability and its presence as an indicator of specific metamorphic conditions make it a subject of interest for both geologists and industrial professionals alike. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the mineral’s physical and chemical properties, its occurrence in nature, its industrial applications, and the various technological advances associated with its use.
Contents
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Andalusite
- Geological Formation, Occurrence, and Geographical Distribution of Andalusite
- Industrial and Commercial Significance of Andalusite
- Recap of Andalusite’s Importance
Physical and Chemical Properties of Andalusite

Andalusite is a mineral with a distinct set of physical and chemical properties that contribute to its unique characteristics and its various industrial applications. These properties determine its appearance, behavior under different conditions, and its role in different industries. Here are the key physical and chemical properties of andalusite:
Physical Properties:
- Crystal Structure: Andalusite crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. Its crystals often have a prismatic habit and can form elongated, columnar shapes. The crystals may also exhibit a cross-shaped pattern due to pleochroism, caused by variations in color along different crystallographic axes.
- Color: Andalusite can vary in color, including green, brown, reddish-brown, gray, and nearly colorless. The pleochroic effect can lead to color variations when the mineral is observed from different angles.
- Luster: The luster of andalusite is usually vitreous to sub-vitreous, giving the mineral a glassy or slightly shiny appearance on its surfaces.
- Hardness: Andalusite has a hardness of 6.5 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, which places it in the range of harder minerals. This property contributes to its durability and resistance to abrasion.
- Cleavage: Andalusite exhibits good cleavage in two directions, intersecting at nearly a right angle. The cleavage planes are not always very prominent, but they can affect the way the mineral breaks along these planes.
- Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of andalusite ranges from approximately 3.15 to 3.20, which is relatively moderate.
- Transparency: Andalusite is usually translucent to opaque, depending on the specimen and its impurities. Transparent andalusite crystals are less common.
Chemical Properties:
- Chemical Formula: The chemical formula of andalusite is Al2SiO5, indicating its composition of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O) atoms.
- Silicate Structure: Andalusite is a silicate mineral, belonging to the aluminosilicate subgroup. Its crystal structure consists of tetrahedral silicon and aluminum units bonded to oxygen atoms, forming a three-dimensional framework.
- Thermal Stability: One of the most significant chemical properties of andalusite is its exceptional thermal stability. This property is attributed to its unique crystal structure, which allows it to maintain its form and integrity even at high temperatures. This makes it valuable for applications in refractories.
- Pleochroism: Andalusite is pleochroic, meaning it exhibits different colors when viewed from different angles. This property is due to variations in absorption of light along different crystallographic directions.
- Impurities: The color variations in andalusite are often caused by trace elements and impurities present in the mineral’s structure. Carbonaceous material, iron, and other elements can influence its coloration.
Understanding these physical and chemical properties is crucial for both identifying andalusite and harnessing its properties for various industrial applications. Its unique combination of characteristics, particularly its thermal stability and pleochroism, make it a versatile and sought-after material in sectors such as refractories, ceramics, and more.
Geological Formation, Occurrence, and Geographical Distribution of Andalusite

Geological Formation: Andalusite forms under specific metamorphic conditions involving high temperatures and pressures. It is typically associated with regional or contact metamorphism of aluminum-rich rocks, such as shale, schist, and slate, that have been subjected to significant geological processes. The mineral’s formation is often a result of the recrystallization of aluminum silicate minerals under metamorphic conditions.
Occurrence: Andalusite is found in various geological settings and is often associated with medium- to high-grade metamorphic rocks. It can occur as individual crystals, aggregates, or even as part of larger rock formations. The occurrence of andalusite is linked to the mineral’s stability within specific temperature and pressure ranges. It can also be an indicator of the intensity and depth of regional metamorphism.
Geographical Distribution: Andalusite is distributed globally in various regions with suitable geological conditions. Some of the notable regions where andalusite is found include:
- Andalusia, Spain: The mineral was originally discovered in the Andalusia region of Spain, from which it derives its name. This area remains a historical source of andalusite.
- France: The Lacroix-Saint-Ouen area in France is known for its andalusite-bearing schists.
- South Africa: The Republic of South Africa is a major producer of andalusite, with deposits found in the Limpopo Province and other regions. The country is recognized as a significant supplier of high-quality andalusite for industrial applications.
- Australia: Andalusite is found in several locations across Australia, including New South Wales, South Australia, and Western Australia.
- China: China has andalusite deposits in regions such as Sichuan, Liaoning, and Jiangxi provinces.
- Russia: Russia has deposits of andalusite in the Urals region, particularly in the Ural Mountains.
- Brazil: Andalusite occurrences have been reported in some Brazilian states, including Minas Gerais.
- United States: Andalusite is found in regions of North Carolina and Georgia in the United States.
These are just a few examples of the geographical distribution of andalusite deposits. The mineral’s presence in various countries reflects the global occurrence of suitable metamorphic environments that foster its formation.
Significance: The presence of andalusite in certain rock formations can provide valuable information about the geological history and conditions of a specific region. The mineral’s stability under specific metamorphic conditions and its role as an indicator mineral contribute to its significance in geological studies. Additionally, andalusite’s unique thermal stability and physical properties make it a valuable resource for industries like refractories, ceramics, and more. Its widespread distribution ensures a consistent supply for these industrial applications.
Industrial and Commercial Significance of Andalusite

Andalusite holds significant importance in various industrial sectors due to its exceptional physical properties, particularly its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical reactions. These qualities make andalusite a valuable material for specialized applications that require durability, strength, and resistance to extreme conditions. Here are some of the key industrial and commercial uses of andalusite:
1. Refractories: Andalusite is a critical component in the production of refractory materials, which are designed to withstand high temperatures, corrosive environments, and mechanical stresses. Refractories are essential in industries such as steel, cement, glass, and non-ferrous metal production, where they line furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Andalusite’s exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock make it an ideal choice for refractory applications. It helps maintain the structural integrity of refractory linings, ensuring that they can withstand the extreme conditions present in industrial processes.
2. Ceramics and Porcelain: Andalusite plays a role in the ceramic and porcelain industries due to its ability to enhance the properties of these materials. It can be used as a raw material in the production of high-quality ceramic products. Andalusite’s incorporation into ceramic formulations can improve mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, and overall performance of the final products. In the porcelain industry, andalusite is valued for its contribution to the whiteness and translucency of porcelain, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
3. Foundry Industry: In the foundry industry, andalusite-based refractory materials are used to line crucibles and molds for metal casting processes. The refractories ensure that the molds can withstand the high temperatures required for melting and casting metals without deforming or breaking down. Andalusite’s resistance to molten metals and its stability at high temperatures make it a reliable choice in this application.
4. Glass Manufacturing: Andalusite’s thermal stability and resistance to chemical reactions make it a suitable component in glass manufacturing. It can be added to glass formulations to improve the refractory properties of the glass and enhance its ability to withstand high temperatures during the melting and forming processes.
5. Other Industrial Applications: Andalusite is also used in other specialized applications such as in the production of kiln furniture (supports and structures inside kilns), investment casting, and as a component in some catalysts used in chemical processes.
The industrial and commercial significance of andalusite lies in its ability to contribute to the efficiency, durability, and safety of processes in industries that require high-temperature operations. Its use in refractory materials, ceramics, and other applications helps maintain the integrity of equipment, reduce downtime, and improve the quality of final products. As technology advances and industries continue to demand materials that can withstand extreme conditions, the importance of andalusite remains firmly established.
Other Uses

In addition to its primary industrial applications in refractories, ceramics, and related fields, andalusite has a few other specialized uses in various industries. Here are some of the lesser-known applications of andalusite:
1. Jewelry and Gemstone Use: Although andalusite is not as commonly used in jewelry as other gemstones, it has been cut and polished into cabochons and faceted gems. Its pleochroic nature, which causes it to display different colors from different angles, can make it an intriguing choice for jewelry. However, due to its relative hardness, andalusite is not as durable as some other gemstones, and it’s usually used in jewelry items that won’t be subjected to heavy wear.
2. Metallurgical Additives: Andalusite’s refractory properties extend to its use as an additive in metallurgical processes. It can be incorporated into metallurgical mixtures to enhance the performance of refractory materials used in metal processing and casting.
3. Crystal Healing and Alternative Medicine: In some alternative medicine practices, andalusite is believed to possess healing properties that promote balance and harmony. It is thought to aid in self-realization, self-awareness, and stress relief. However, it’s important to note that the efficacy of these claims lacks scientific evidence and is largely based on metaphysical beliefs.
4. Research and Laboratory Applications: Andalusite’s unique crystal structure and physical properties make it of interest to researchers and scientists studying crystallography, mineralogy, and geology. It can be used as a model mineral in studies that aim to understand crystal growth, phase transitions, and other geological processes.
5. Educational Purposes: Due to its distinctive crystal structure and properties, andalusite is sometimes used in educational settings to help students learn about mineral identification, crystallography, and mineral properties. Its cross-shaped pleochroism, in particular, can be a fascinating visual aid in teaching these concepts.
While these additional uses of andalusite might not be as prevalent or widespread as its primary industrial applications, they showcase the mineral’s versatility and the diverse ways in which it can be utilized across various domains.
Recap of Andalusite’s Importance
 BRAZILIAN ANDALUSITE 8.39CT 14.33X11.58X7.55MM OVAL
BRAZILIAN ANDALUSITE 8.39CT 14.33X11.58X7.55MM OVAL
- Exceptional Thermal Stability: Andalusite’s remarkable ability to maintain its integrity under high temperatures and thermal shock makes it a critical component in refractories used to line furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment.
- Refractories and High-Temperature Applications: The mineral’s use in refractories is crucial for industries such as steel, cement, glass, and non-ferrous metal production, where it ensures the durability and longevity of materials in extreme heat and corrosive environments.
- Ceramics and Porcelain: Andalusite’s inclusion in ceramics and porcelain formulations enhances the mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, and aesthetic qualities of these products, contributing to their quality and performance.
- Indicator of Metamorphic Conditions: In the field of geology, andalusite’s presence serves as an indicator of specific metamorphic conditions, helping researchers understand the geological history and processes of specific regions.
- Unique Pleochroism: Its distinct pleochroic effect, causing it to display different colors from different angles, contributes to its value as a gemstone and educational tool for teaching mineral identification and crystallography.
- Specialized Industrial Uses: Andalusite is used in various other applications, including the foundry industry for metal casting, glass manufacturing, and as a component in some catalysts.
- Global Distribution: The mineral’s widespread occurrence in regions around the world ensures a consistent supply for industrial and scientific purposes.
- Research and Education: Andalusite’s unique properties also make it of interest to researchers studying crystal growth, mineralogy, and related fields. It serves as an educational tool for teaching mineral properties and crystallography.
- Aesthetic and Metaphysical Uses: Andalusite, though not as commonly used, is sometimes cut and polished for jewelry and is believed to possess metaphysical healing properties in alternative medicine practices.
In essence, andalusite’s importance lies in its role as a versatile material that contributes to the success of industries requiring high-temperature materials, as well as its significance in scientific research and educational endeavors. Its rich history, unique properties, and wide range of applications make it a mineral of enduring value.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!