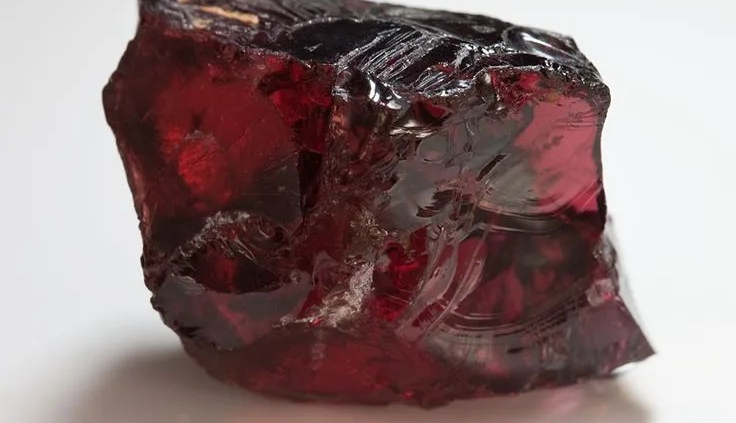
Pyrope Garnet
Pyrope garnet is a fascinating gemstone known for its stunning deep red color and remarkable beauty. It belongs to the garnet family, a group of minerals renowned for their diverse range of colors, and pyrope is specifically recognized for its vibrant red hues.



Definition: Pyrope garnet is a variety of garnet that is primarily characterized by its vivid red color. It is one of the most well-known and sought-after gemstones within the garnet family. The name “pyrope” is derived from the Greek words “pyr,” meaning fire, and “ops,” meaning eye, due to its fiery and brilliant appearance.
Contents
- Physical, Chemical and Optical Properties of Pyrope Garnet
- Formation and Occurrence of Pyrope
- Geological Sources and Global Distribution
- Pyrope Garnet Varieties
- Uses and Applications
- Gemological Characteristics
- Market Trends and Value
Physical, Chemical and Optical Properties of Pyrope Garnet
Pyrope garnet possesses several physical, chemical, and optical properties that make it a unique and valuable gemstone. Here are some of its key characteristics in each of these categories:
Physical Properties:
- Color: Pyrope garnet is renowned for its intense red to purplish-red color, which can range from a deep crimson to a rich wine-red. The color is often uniform and saturated.
- Hardness: It has a hardness of 7 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively durable and suitable for use in various types of jewelry, including rings and earrings.
- Crystal System: Pyrope garnet belongs to the isometric crystal system, typically forming in the shape of dodecahedrons or trapezohedrons.
- Cleavage: Pyrope garnet lacks significant cleavage, which means it doesn’t easily split along specific planes when subjected to stress.
- Luster: It exhibits a vitreous (glass-like) to resinous luster when polished.
Chemical Properties:
- Chemical Composition: Pyrope garnet has the chemical formula Mg3Al2(SiO4)3. It is a silicate mineral and is part of the larger garnet group.
- Color-causing Elements: The vivid red color of pyrope garnet is often attributed to trace amounts of chromium (Cr) in its crystal structure. The presence of chromium ions is responsible for the gem’s red fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
Optical Properties:
- Refractive Index (RI): Pyrope garnet typically has a refractive index ranging from approximately 1.71 to 1.75. This property contributes to its brilliance and the way it interacts with light.
- Birefringence: Pyrope garnet is non-birefringent, which means it does not split incident light into two different rays as some other minerals do. This optical property helps maintain its single, sharp image when viewed through a gemstone.
- Dispersion: While pyrope garnet does exhibit some dispersion (the separation of white light into its spectral colors), it is not as pronounced as in some other gemstones like diamond or zircon.
- Transparency: It is usually transparent to translucent, with higher-quality specimens being more transparent.
- Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of pyrope garnet typically ranges from 3.5 to 4.3, depending on the specific chemical composition and impurities present.
- Optical Phenomena: In some rare cases, pyrope garnet may display asterism (a star-like effect) when cut into cabochon shapes, especially if the gem contains inclusions of oriented rutile or other needle-like minerals.
These physical, chemical, and optical properties collectively contribute to the beauty and desirability of pyrope garnet as a gemstone, making it a popular choice for jewelry and collectors alike.
Formation and Occurrence of Pyrope

Pyrope garnet forms through geological processes involving high temperatures and pressure conditions. Its occurrence is often associated with specific rock types and environments. Here’s an overview of the formation and occurrence of pyrope garnet:
Formation:
- Metamorphism: Pyrope garnet typically forms in metamorphic rock environments. Metamorphism occurs when pre-existing rocks undergo changes in temperature and pressure deep within the Earth’s crust. These changes can lead to the growth of garnet crystals.
- Parent Rocks: Pyrope garnet is often found in rocks such as eclogite, a high-pressure, high-temperature metamorphic rock, and peridotite, an ultramafic rock. These parent rocks contain the necessary components for garnet formation, including magnesium (Mg) and aluminum (Al).
- Mineral Reactions: The formation of pyrope garnet is the result of complex mineral reactions that involve the interaction of various minerals within the parent rocks. Under high-pressure conditions, minerals like pyroxenes and olivine can react with one another, releasing components like aluminum and silica (SiO2), which are essential for garnet formation.
- Crystallization: As the chemical components necessary for garnet formation become available due to mineral reactions, garnet crystals begin to grow. The high-pressure environment promotes the formation of garnet with its characteristic crystal structure.
Occurrence:
- Geographical Distribution: Pyrope garnet is found in various locations around the world. Some of the notable sources include the following:
- United States: Pyrope garnets are found in regions like Arizona and New Mexico.
- South Africa: The famous “Cape Ruby” deposits in the Western Cape Province are known for producing pyrope garnets.
- Madagascar: Pyrope garnets are found in several locations across Madagascar.
- Myanmar (Burma): Myanmar has historically been a significant source of fine-quality pyrope garnets.
- Mozambique: Mozambique is known for producing pyrope garnets with exceptional color and clarity.
- Alluvial Deposits: In some cases, pyrope garnets are eroded from their primary sources by weathering and transported by rivers and streams. These alluvial deposits can be a source of garnets that are later collected by gemstone miners.
- Mining: The extraction of pyrope garnets involves mining in areas where they are known to occur. Miners may use various methods, including open-pit mining and underground mining, to access the gem-bearing rocks.
- Quality Variations: The quality of pyrope garnets can vary significantly based on their source. Some locations produce gems with exceptional color and clarity, while others may yield stones with more modest characteristics.
In summary, pyrope garnet forms through metamorphic processes in specific rock types, and its occurrence can be found in various locations globally. The geological conditions in these areas are essential for the formation and preservation of this beautiful gemstone.
Geological Sources and Global Distribution

Pyrope garnets are primarily found in metamorphic rocks, particularly in high-pressure, high-temperature environments. They are often associated with specific rock types like eclogite and peridotite, which provide the necessary elements for garnet formation. Here’s a look at the global distribution and notable deposits of pyrope garnet:
1. United States: Pyrope garnets are found in several states, including Arizona, New Mexico, and Colorado. Notable locations include the Garnet Ledge in New Mexico.
2. South Africa: South Africa is known for its “Cape Ruby” deposits in the Western Cape Province, where pyrope garnets are extracted.
3. Madagascar: Pyrope garnets are found in several regions of Madagascar, particularly in the southern part of the island.
4. Myanmar (Burma): Myanmar has historically been a significant source of high-quality pyrope garnets, often referred to as “Burmese rubies.”
5. Mozambique: Mozambique is known for producing pyrope garnets with exceptional color and clarity. The Montepuez area in Mozambique is renowned for its red garnets.
6. Russia: Some pyrope garnets are found in Russia, including the Ural Mountains region.
7. Australia: Pyrope garnets have been found in Western Australia, particularly in the Kimberley region.
8. China: Pyrope garnets are occasionally found in various provinces in China.
9. India: India is another country where pyrope garnets have been discovered, although they are not as well-known as other gemstones from the region.
Notable Deposits:
- Bohemian Garnets: The Bohemian region in the Czech Republic has been a historically significant source of pyrope garnets, known as “Bohemian garnets.” These gems were popular in European jewelry during the 19th century.
- Jeffrey Mine (Canada): The Jeffrey Mine in Quebec, Canada, was a renowned source of pyrope garnets, including large and high-quality specimens. However, the mine has closed, and the material is now considered a collector’s item.
Mining and Extraction:
Mining and extracting pyrope garnets involve various methods, depending on the deposit type and location. Here are some common methods:
- Open-Pit Mining: In many cases, pyrope garnets are mined through open-pit mining, where the gem-bearing rock is excavated from the surface.
- Underground Mining: Some deposits may require underground mining to access pyrope-bearing rocks. This method is used when the deposit is too deep for open-pit mining.
- Alluvial Mining: Alluvial deposits, where garnets are eroded from their primary source and transported by rivers, can be mined through placer mining techniques.
- Hand-Picking: In some cases, particularly in alluvial deposits, miners may use hand-picking to select garnets from gravels and sediments.
- Mechanical Sorting: Mechanical methods, such as screens and conveyors, are sometimes employed to separate garnets from other minerals and materials.
Once extracted, pyrope garnets are sorted, graded, and cut for use in jewelry and other decorative purposes. The quality of the garnets is assessed based on factors like color, clarity, size, and overall appearance, with the finest specimens commanding the highest value in the gemstone market.
Pyrope Garnet Varieties
 Arizona Pyrope
Arizona Pyrope
Pyrope garnet is known for its striking red color, but within this category, there can be some variations and unique varieties based on factors like color, origin, and certain properties. Here are a few notable pyrope garnet varieties:
- Cape Ruby: The term “Cape Ruby” is often used to describe pyrope garnets from South Africa, particularly those from the Western Cape Province. These garnets are known for their intense red color, often resembling the rich hue of fine rubies.
- Bohemian Garnet: This term refers to pyrope garnets from the Bohemian region in the Czech Republic. Bohemian garnets were highly prized in the 19th century and were used extensively in jewelry during that period. They are known for their deep red color and have historical significance.
- Arizona Pyrope: Pyrope garnets found in Arizona, USA, are sometimes referred to as “Arizona Pyrope.” They can exhibit a range of red shades, from medium to dark red, and are often used in jewelry.
- Malaya Garnet: Malaya garnet is a variety of pyrope garnet that is valued for its color-changing properties. It can shift in color from pinkish-orange in daylight to reddish-purple under incandescent lighting. This unique characteristic makes Malaya garnet highly sought after by gem enthusiasts.
- Umbalite Garnet: Umbalite garnet is a specific type of pyrope garnet known for its vivid purplish-red to pinkish-red color. It is typically found in the Umba Valley of Tanzania and is admired for its vibrant and attractive hues.
- Mozambique Garnet: Pyrope garnets from Mozambique are well-regarded for their bright red color and good clarity. They have gained popularity in the gemstone market and are often used in jewelry designs.
- Montana Garnet: Found in the state of Montana, USA, these pyrope garnets can range from deep red to purplish-red. Montana garnets are known for their alluvial deposits, which can yield small to medium-sized gems.
- Myanmar (Burmese) Pyrope: Pyrope garnets from Myanmar (formerly Burma) are often referred to as “Burmese Pyrope.” They are esteemed for their rich red color and are considered among the finest pyrope garnets in terms of color quality.
These varieties of pyrope garnet offer gem enthusiasts and jewelry designers a range of options when it comes to color and appearance. Each variety may have its own unique appeal and can be used to create stunning jewelry pieces. The desirability of a specific variety often depends on individual preferences for color and rarity.
Uses and Applications

Pyrope garnet is a versatile gemstone with various uses and applications, primarily in the field of jewelry and as collector’s items. Here are some of the common uses and applications of pyrope garnet:
- Jewelry: Pyrope garnet’s vibrant red color and relatively high hardness make it a popular choice for jewelry. It is often used in rings, earrings, necklaces, pendants, and bracelets. Pyrope garnet can be faceted into various shapes, including rounds, ovals, and cushion cuts, to create beautiful gemstone jewelry pieces.
- Gemstone Collecting: Pyrope garnets, especially those with exceptional color and clarity, are highly sought after by gemstone collectors. Collectors appreciate the variety of pyrope garnet types, including Cape Ruby, Bohemian garnet, and Malaya garnet, for their unique characteristics and historical significance.
- Birthstone: Pyrope garnet is one of the birthstones for the month of January. It is often incorporated into birthstone jewelry pieces, such as rings or pendants, as a thoughtful and personalized gift for individuals born in that month.
- Investment: Some collectors and investors view high-quality pyrope garnets as potential investments. The value of gem-quality pyrope garnets can appreciate over time, particularly if they are rare, exhibit exceptional color, or have historical significance.
- Lapidary Arts: Pyrope garnet is a favorite among lapidaries and gemstone artists who use it to create custom-cut gemstones for jewelry design. Its bright red color and attractive luster make it a valuable material for lapidary projects.
- Metaphysical and Spiritual Beliefs: In some cultures, certain gemstones, including pyrope garnet, are believed to possess metaphysical and healing properties. Pyrope garnet is associated with qualities such as passion, energy, and protection, and it is thought to bring positive energy to the wearer.
- Historical and Antique Jewelry: Antique and vintage jewelry pieces often feature pyrope garnets, especially Bohemian garnets, which were widely used in jewelry during the 19th century. These historical pieces are highly collectible and have cultural and historical significance.
- Fashion Accessories: Pyrope garnet can be used as accents or focal points in fashion accessories like brooches, hairpins, and tiaras, adding a touch of elegance and color to couture designs.
It’s important to note that while pyrope garnet is a durable gemstone suitable for everyday wear, it should be cared for properly to maintain its beauty and value. Like all gemstones, pyrope garnet can benefit from regular cleaning and safe storage when not in use.
Overall, pyrope garnet’s vivid red color, versatility, and historical appeal have ensured its continued popularity in the world of gemstones and jewelry.
Gemological Characteristics

Gemological characteristics are specific attributes and properties used to assess and describe gemstones, including pyrope garnet. These characteristics help gemologists, jewelers, and buyers evaluate the quality, authenticity, and value of a gemstone. Here are the key gemological characteristics for pyrope garnet:
- Color:
- Pyrope garnet is known for its intense red to purplish-red color. The quality and desirability of the color depend on factors like saturation, hue, and tone.
- The most sought-after pyrope garnets exhibit a pure and vivid red color with strong saturation. Darker red hues are generally more valuable.
- Exceptional color in pyrope garnets is sometimes referred to as “Cape Ruby” when it closely resembles the color of fine rubies.
- Clarity:
- Clarity refers to the presence of internal inclusions and external blemishes or imperfections in the gemstone.
- Pyrope garnets are often relatively free of significant inclusions, but some stones may contain tiny internal features or surface imperfections.
- Gems with higher clarity, especially when they are eye-clean (appear free of visible inclusions to the naked eye), are considered more valuable.
- Cut:
- The cut of a pyrope garnet can significantly impact its appearance and overall beauty. Well-cut pyrope garnets exhibit excellent brilliance and sparkle.
- Common cuts for pyrope garnets include faceted shapes like round, oval, cushion, and emerald cut.
- The cut should maximize the gem’s color and minimize any extinction (dark areas) within the stone.
- Carat Weight:
- Carat weight measures the size of the gemstone. Larger pyrope garnets are rarer and can command higher prices.
- Gem-quality pyrope garnets are often available in a range of sizes, from small accent stones to larger focal points in jewelry.
- Refractive Index (RI):
- The refractive index of pyrope garnet typically ranges from approximately 1.71 to 1.75. This property affects how light interacts with the gem and contributes to its brilliance.
- Dispersion:
- Pyrope garnet exhibits some dispersion, which refers to the gem’s ability to separate white light into its spectral colors (fire). While not as pronounced as in some other gemstones like diamond, it can still enhance the gem’s visual appeal.
- Luster:
- Pyrope garnet has a vitreous (glass-like) to resinous luster when polished. This luster contributes to its shine and brilliance.
- Hardness:
- Pyrope garnet has a hardness of 7 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively resistant to scratching and suitable for use in various types of jewelry.
- Specific Gravity:
- The specific gravity of pyrope garnet typically ranges from 3.5 to 4.3, depending on its chemical composition and impurities. Specific gravity helps in distinguishing it from other gemstones with similar appearance.
- Optical Phenomena:
- Some pyrope garnets can exhibit optical phenomena such as asterism (a star-like effect) when cut into cabochon shapes. This occurs when the gem contains inclusions of oriented rutile or other needle-like minerals.
- Fluorescence:
- Pyrope garnets may exhibit fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly if they contain trace amounts of chromium.
Understanding these gemological characteristics is essential when evaluating and purchasing pyrope garnet or any gemstone, as they determine the gem’s quality, value, and suitability for various jewelry and ornamental purposes.
Market Trends and Value

Market trends and the value of pyrope garnet can fluctuate based on various factors, including supply and demand, gem quality, consumer preferences, and market dynamics. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, I can provide some insights into the general market trends and factors affecting the value of pyrope garnet:
Market Trends:
- Rarity and Collectibility: Pyrope garnet, particularly high-quality specimens with vivid red or purplish-red colors, is considered rare and collectible. Gem enthusiasts and collectors seek out these exceptional gems.
- Gem Identification: Advances in gemological testing and identification techniques have allowed for more accurate classification of pyrope garnets. This has led to a better understanding of their characteristics and improved market transparency.
- Fashion and Jewelry Trends: The popularity of pyrope garnet in jewelry can be influenced by fashion and design trends. When red gemstones are in vogue, pyrope garnet tends to gain more attention.
- Origin Matters: The geographic source of pyrope garnet can affect its market value. For example, stones from historically significant locations like Bohemian garnets or Burmese pyrope garnets may command higher prices due to their heritage and scarcity.
Factors Affecting Value:
- Color: The most critical factor influencing the value of pyrope garnet is its color. Gems with a pure, vibrant, and deeply saturated red or purplish-red hue are considered the most valuable.
- Clarity: Gems with higher clarity, especially those that are eye-clean (without visible inclusions to the naked eye), are more valuable.
- Size: Larger pyrope garnets are rarer and can command higher prices per carat compared to smaller stones.
- Cut Quality: A well-executed cut that maximizes the gem’s color and brilliance can enhance its value.
- Origin: Some collectors and buyers may place a premium on pyrope garnets from specific historical or renowned sources.
- Treatment: Untreated pyrope garnets are generally more valuable than those that have undergone enhancements, such as heat treatment.
- Market Demand: Current market demand for pyrope garnet can influence its price. Trends in the jewelry market, consumer preferences, and marketing efforts can all impact demand.
- Gemological Reports: Having a reputable gemological report from a recognized laboratory that confirms the gem’s quality and authenticity can add value and trust in the marketplace.
It’s essential to note that gemstone markets can change over time, and specific market trends and values may have evolved since my last knowledge update in September 2021. To obtain the most current information on pyrope garnet market trends and values, it is advisable to consult with gemstone experts, gemological laboratories, and industry publications. Additionally, working with reputable jewelers and gem dealers can help you make informed decisions when buying or selling pyrope garnet.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!