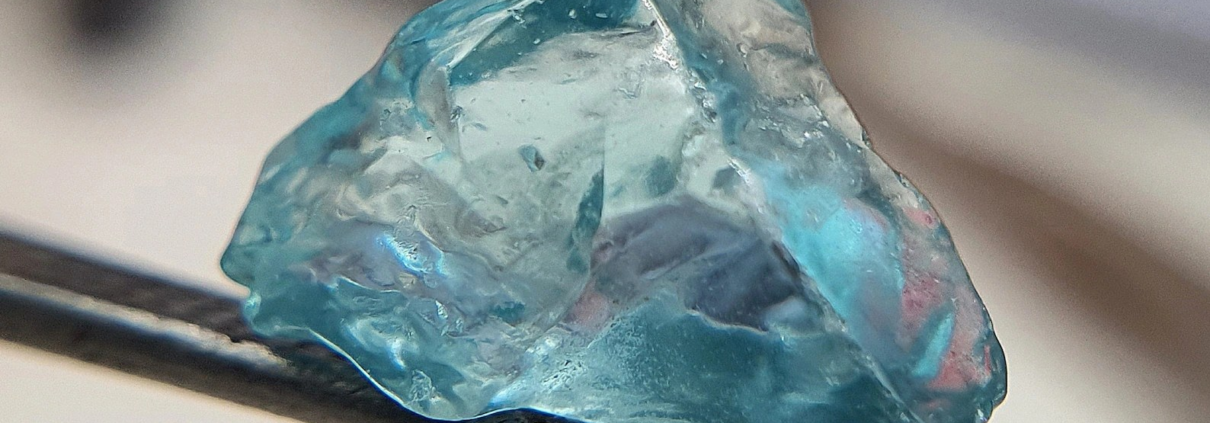
Blue Zircon
Blue zircon is a beautiful and captivating gemstone that has gained popularity in the world of jewelry. It is known for its striking blue hues and exceptional brilliance, making it a sought-after choice for various jewelry pieces.
 Blue Zircon
Blue Zircon
Blue zircon is a naturally occurring gemstone belonging to the zircon family. It is characterized by its vibrant blue colors, which range from pale blue to deep azure, and is widely recognized for its intense sparkle and high refractive index. Zircon is a mineral composed of zirconium silicate and can be found in a variety of colors, with blue zircon being one of the most valued varieties.
Blue zircon’s stunning color is attributed to the presence of trace elements such as uranium and thorium during its formation. These elements cause the gem to absorb certain wavelengths of light and emit a captivating blue glow. Blue zircons are typically faceted to enhance their brilliance, and they are used in various forms of jewelry, including rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.
Significance and Popularity of Blue Zircon in Jewelry:
- Vivid and Attractive Color: Blue zircon’s vivid and alluring blue hues make it a highly desirable gemstone in the world of jewelry. The gem’s brilliance and captivating play of colors under different lighting conditions give it an eye-catching appeal.
- December Birthstone: Blue zircon is one of the accepted birthstones for the month of December, making it a popular choice for individuals born in this month. It is often associated with qualities like wisdom, honor, and prosperity.
- Affordability: Blue zircon offers an affordable alternative to other blue gemstones like sapphires and aquamarines. It provides the opportunity for individuals to own a beautiful blue gemstone without the high price tag associated with some other options.
- Durability: Zircon is a relatively hard gemstone with good durability, making it suitable for everyday wear in various types of jewelry. However, like all gemstones, it should be handled with care to avoid damage.
- Historical and Cultural Significance: Zircon has a rich history and has been used in jewelry for centuries. In some cultures, it was believed to have healing properties and spiritual significance. It has been associated with protecting travelers, promoting wisdom, and enhancing one’s spirituality.
- Versatility: Blue zircon can be set in various metals, including white gold, yellow gold, and platinum, allowing for diverse design options in jewelry. Its vibrant color can be complemented with diamonds or other gemstones, adding to its versatility in design.
In conclusion, blue zircon is a captivating gemstone known for its brilliant blue color and remarkable sparkle. Its significance as a birthstone, affordability, durability, and cultural importance make it a popular choice for jewelry designers and enthusiasts alike. Whether used as the focal point or in combination with other gemstones, blue zircon continues to be a favored option for creating exquisite and stylish jewelry pieces.
Contents
- Geological Formation
- Characteristics of Blue Zircon
- Sources and Mining
- Alternatives and Comparisons
Geological Formation

Geological Formation of Zircon Gemstones: Zircon gemstones are minerals that form through complex geological processes. They are typically found in a variety of colors, including blue, and their formation is closely tied to igneous and metamorphic rock environments. Here’s an overview of the geological formation of zircon gemstones:
- Magmatic Origin: The primary formation of zircon occurs in magmatic rocks, such as granite and syenite. Zircon crystals are often found within these rocks, and they start as small grains or crystals embedded in the molten rock material.
- High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions: Zircon formation takes place under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, typically deep within the Earth’s crust. These conditions promote the growth of zircon crystals from the mineral-rich melt.
- Chemical Composition: Zircon is composed of zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4). During the crystallization process, zirconium and silicon atoms combine with oxygen to form the distinct crystal structure of zircon.
- Accessory Minerals: Zircon often forms alongside other minerals, and it can incorporate trace elements during its growth. These trace elements can influence the color of the zircon crystal, leading to various colors, including the prized blue color.

Factors Contributing to the Blue Color in Zircon: The blue color in zircon gemstones is a result of the presence of specific trace elements and the way they interact with the crystal structure. Several factors contribute to the blue coloration in zircon:
- Uranium: Uranium is one of the key trace elements responsible for the blue color in zircon. Uranium atoms can replace some of the zirconium atoms within the crystal lattice. This substitution creates localized radiation damage within the crystal, leading to the absorption of certain wavelengths of light in the visible spectrum and the emission of a blue color.
- Thorium: Thorium can also be present in zircon and contribute to the blue coloration. Like uranium, thorium atoms can substitute for zirconium, leading to radiation-induced color centers that result in the blue hue.
- Natural Radiation Exposure: Over geological time, zircon crystals are exposed to natural radioactivity from elements like uranium and thorium present in the surrounding rocks. This radiation causes the crystal lattice to develop defects and accumulate damage, ultimately leading to the blue color.
- Crystal Structure: The crystal structure of zircon itself plays a role in the blue color. Zircon’s tetragonal crystal structure and the presence of impurities and defects create a favorable environment for the absorption and emission of blue light.
It’s important to note that not all zircon gemstones exhibit a blue color; zircon can be found in various colors, including red, brown, and green, depending on the specific trace elements present and their concentration. Blue zircon, with its intense and captivating color, is particularly prized in the world of gemstones and jewelry.
Characteristics of Blue Zircon

Blue zircon is a captivating gemstone known for its unique characteristics, making it a popular choice in the world of jewelry. Here are the key characteristics of blue zircon:
- Color: The most distinctive feature of blue zircon is its striking blue color. It can range from pale and icy blues to deep and vibrant azure shades. The color can be compared to that of a clear blue sky or a calm ocean, and it is often described as intense and alluring.
- Brilliance and Luster: Blue zircon is prized for its exceptional brilliance and luster. It exhibits a high refractive index, which means it reflects and refracts light brilliantly, creating a sparkling, lively appearance.
- Transparency: Blue zircon is typically transparent, allowing light to pass through the gemstone and contribute to its radiance. This transparency enhances its beauty and appeal.
- Faceting: To maximize its brilliance and play of color, blue zircon is commonly cut into various faceted shapes, such as rounds, ovals, cushions, and emerald cuts. The cutting style enhances the gem’s natural beauty.
- Durability: Zircon is relatively hard, with a hardness rating of 6.5 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale. While it is not as hard as some other gemstones like sapphire or diamond, it is still suitable for use in various types of jewelry, including rings, earrings, necklaces, and bracelets. Care should be taken to prevent scratches and other damage.
- Dispersion: Blue zircon exhibits a high degree of dispersion, which means it has the ability to break white light into its spectral colors, creating flashes of fire within the gem. This dispersion contributes to its impressive play of colors.
- Pleochroism: Some blue zircon may display pleochroism, meaning it can exhibit different shades of blue when viewed from different angles. This optical effect adds depth and complexity to the gem’s appearance.
- Size and Clarity: Blue zircon is available in a wide range of sizes, from small accent stones to larger centerpiece gems. The gem’s clarity can also vary, with some stones being relatively free of inclusions, while others may have minor inclusions.
- Affordability: Blue zircon is often more affordable than other blue gemstones like sapphires and aquamarines, making it an attractive option for those looking for a beautiful blue gemstone without the higher price tag.
- Birthstone: Blue zircon is recognized as one of the December birthstones, and it is often associated with qualities such as wisdom, honor, and prosperity. This birthstone significance adds to its popularity.
In summary, blue zircon is cherished for its vibrant blue color, outstanding brilliance, transparency, and unique optical properties. Its durability and affordability make it a favored choice for a wide range of jewelry designs, and its status as a birthstone for December adds to its desirability.
Sources and Mining

Blue zircon is primarily sourced through mining in various regions around the world. The mining of zircon involves extracting the gemstone from its natural geological deposits. Here’s an overview of the sources and mining of blue zircon:
- Cambodia: Cambodia is known for producing some of the finest blue zircon gemstones. The Ratanakiri province in northeastern Cambodia is a significant source of high-quality blue zircon. The zircon deposits in this region often yield intense blue hues, making them highly sought after in the jewelry industry.
- Sri Lanka: Sri Lanka is another notable source of blue zircon. The gemstone is found in the gem-rich areas of Sri Lanka, including the Ratnapura district. Sri Lankan blue zircon is known for its brilliant color and transparency.
- Australia: Australia, particularly the state of Queensland, is a source of blue zircon. Deposits are found in alluvial sediments, and the gemstones are known for their bright, clean appearance and attractive blue shades.
- Myanmar (Burma): Myanmar has historically been a source of zircon gemstones, including blue zircon. These gems are often found in the Mogok region, which is famous for its gemstone deposits.
- Tanzania: The Umba Valley in Tanzania is known for producing blue zircon with a range of blue shades. Tanzanian blue zircon is popular for its deep and vivid blue colors.
- Madagascar: Madagascar is another source of blue zircon, and the gemstones are typically found in alluvial deposits in the Ilakaka region. Madagascar’s blue zircon is appreciated for its rich blue hues.
- Vietnam: Blue zircon is also mined in Vietnam, with deposits located in the Quy Chau district. Vietnamese zircon is known for its diverse range of colors, including appealing blues.

Mining Methods: The mining of blue zircon typically involves both open-pit and alluvial mining methods. These methods may include:
- Open-Pit Mining: In regions with zircon deposits found in hard rock, open-pit mining is employed. This method involves removing overburden to access the zircon-bearing rock. Miners extract the rock, which is then processed to extract the zircon crystals.
- Alluvial Mining: In alluvial deposits, zircon is eroded from its source rock over time and transported by natural processes like rivers. Miners search for zircon in sediment, gravels, and riverbeds. Alluvial mining is often used to recover zircon in areas where the gemstones have been transported by water.
- Gem Gravel Washing: In alluvial mining, gem gravel washing is a common technique. Miners gather gravel and wash it to separate the valuable zircon crystals from other materials like sand and clay.
- Artisanal Mining: In some regions, particularly in developing countries, artisanal miners use basic tools and methods to extract zircon. This can involve hand digging and simple washing processes.
It’s important to note that the environmental and ethical considerations surrounding gemstone mining are significant. Sustainable and responsible mining practices are essential to minimize the impact on the environment and ensure fair labor practices. Additionally, the gemstone industry often emphasizes transparency and traceability to ensure that gemstones, including blue zircon, are ethically sourced.
Alternatives and Comparisons

When considering blue zircon for jewelry, it’s essential to be aware of alternatives and make comparisons to choose the gemstone that best suits your preferences and requirements. Here are some alternatives to blue zircon, along with comparisons to help you make an informed decision:
- Blue Zircon vs. Blue Topaz:
- Blue Topaz: Blue topaz is a popular and more common blue gemstone. It is available in various shades of blue, from pale to deep blue.
- Comparison: Blue zircon generally has higher brilliance and fire compared to blue topaz. Zircon’s dispersion and luster often make it more appealing for those seeking a vibrant and dazzling gem. However, blue topaz is a more affordable option and is relatively easy to find in various jewelry designs.
- Blue Zircon vs. Sapphire:
- Sapphire: Sapphires are renowned for their durability and deep blue color. They are considered one of the “big four” precious gemstones.
- Comparison: Sapphires are more durable than zircon and have a higher hardness on the Mohs scale. They also come in a wide range of blue shades. However, blue zircon offers a brilliant play of colors and is generally more affordable than sapphires. Zircon’s unique sparkle and dispersion can be an attractive alternative for those looking for a unique and vibrant blue gemstone.
- Blue Zircon vs. Aquamarine:
- Aquamarine: Aquamarine is a popular pale blue or blue-green gemstone known for its soothing and tranquil appearance.
- Comparison: Aquamarine and blue zircon have different color intensities. While blue zircon is known for its intense blue hues, aquamarine has a softer, more pastel blue or greenish-blue color. The choice between them depends on the desired color intensity and personal taste.
- Blue Zircon vs. Blue Tourmaline:
- Blue Tourmaline: Blue tourmaline, such as indicolite, is a blue gemstone known for its unique color and transparency.
- Comparison: Blue zircon has a more intense blue color, while blue tourmaline can have a greenish-blue or teal color. Blue tourmaline may be preferred by those who appreciate its specific color variations, but blue zircon is often chosen for its brilliant and vivid blue.
- Blue Zircon vs. Blue Spinel:
- Blue Spinel: Blue spinel is a durable and attractive gemstone with varying shades of blue.
- Comparison: Blue spinel can offer a similar level of brilliance and sparkle to blue zircon. Both are durable and suitable for jewelry. The choice between the two may come down to personal preference regarding their distinct color and character.
- Blue Zircon vs. Blue Sapphire Simulants:
- Blue Sapphire Simulants: Some gemstones, such as blue synthetic sapphires or other blue gemstone imitations, are created to mimic the appearance of blue sapphires.
- Comparison: Blue zircon is a genuine gemstone with its unique qualities, while simulants, like synthetic sapphires, aim to replicate the look of more expensive gemstones. The choice between the two depends on whether you prefer a natural gemstone with its characteristics or an affordable alternative.
Ultimately, the choice between blue zircon and its alternatives depends on your preferences for color intensity, brilliance, durability, and budget. Each gemstone has its own unique qualities and charm, so it’s essential to consider what matters most to you in your jewelry selection.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!